Question
Question: which gives the most valid and recent explanation for stomatal movements? A.Starch hydrolysis B....
which gives the most valid and recent explanation for stomatal movements?
A.Starch hydrolysis
B.Guard cell photosynthesis
C.Transpiration
D.Potassium influx and efflux
Solution
Stomata are pores on the aerial surface of the plant tissues. The pore opens to help in the uptake of carbon dioxide and close in order to prevent loss of water. The movement in stomata occurs due to the changes in the volume of the guard cell. They are present on either side of the stomatal pores.
Complete answer:
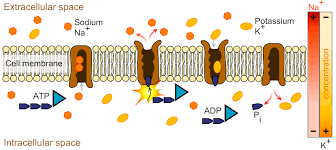
The stomata open in the light to enable photosynthesis and the pores during drought. During the opening, the guard cells accumulate potassium ions which causes osmotic uptake of water. Due to the influx the guard cells swell and bend, thus pushing each other apart that creates an open pore in the middle. This then helps in intake of carbon dioxide. The turgidity of guard cells induces to open the pores of stomata found on the surface of leaves. The increase of K⁺ results in opening of the stoma and decrease of K⁺ causes closing of the stomata. Apart from this there are various environmental signals, such as light, carbon dioxide and humidity that influence the ion transport machinery within the guard cell and thus, alter stomatal movement.
Among the given options:
Starch Hydrolysis The purpose is to check if the microbe can use starch, a complex carbohydrate made from glucose, as a source of carbon and energy for growth or not.
Photosynthesis in guard cells is essential for guard cell turgor production and limited capacity to perform photosynthesis compared to mesophyll cell.
Transpiration is the process of water movement through a plant and its evaporation from aerial parts, such as leaves and stem. Water is necessary for plants but about99% is evaporated during transpiration and only a small amount of water taken up is used for growth and metabolism.
Guard cells are cells surrounding each stoma. This turgidity is caused by the accumulation of K+ (potassium ions) in the guard cells. As K+ levels increase in the guard cells, the water potential of the guard cells drops, and water enters the guard cells.
Hence the correct answer is option D.
Additional information:
Stomata are absent in liverworts. In vascular plants the number, size and distribution of stomata varies widely. In dicotyledons there are more stomata on the lower surface of the leaves than the upper surface.
Note:
Stomata are composed of a pair of specialized epidermal cells referred to as guard cells. Stomata regulate gas exchange between the plant and environment and control of water loss by changing the size of the stomatal pore.
