Question
Question: Which curve corresponds to the temperature dependence of the rate R of a simple one step reaction? ...
Which curve corresponds to the temperature dependence of the rate R of a simple one step reaction?
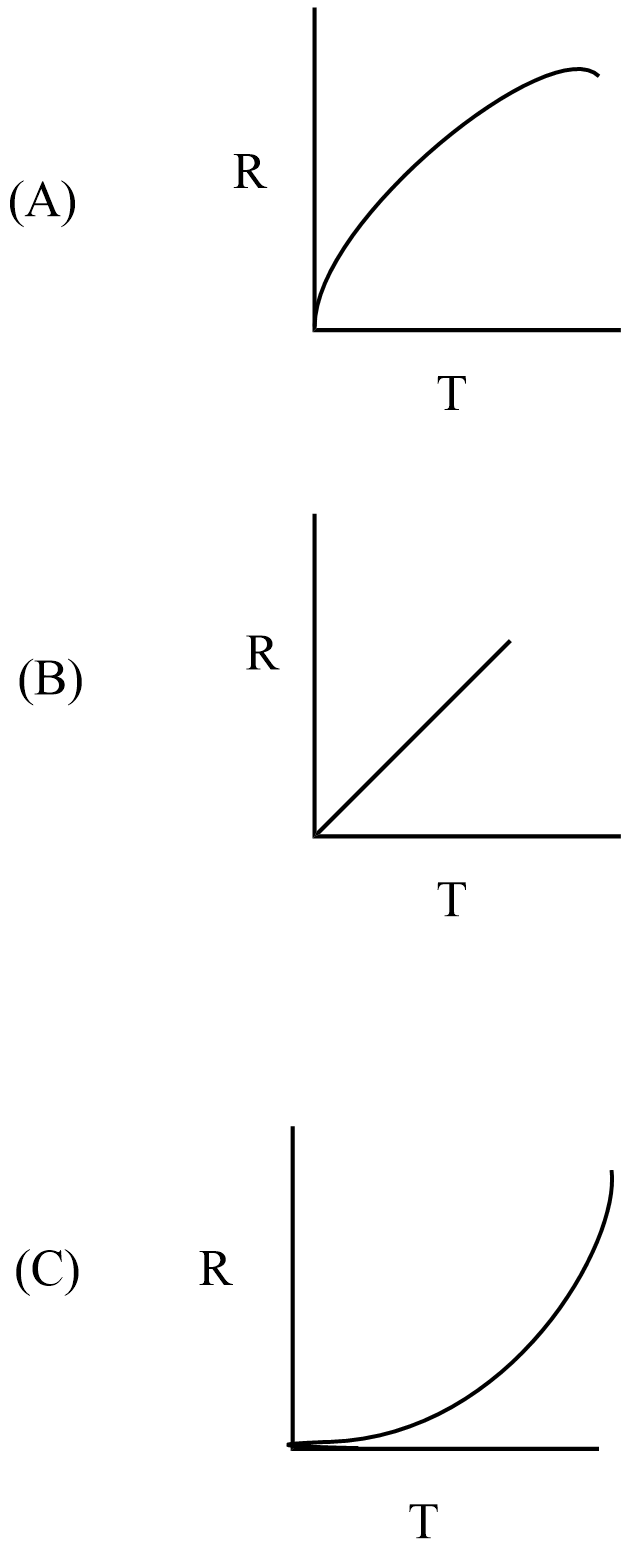
(D) None of these
Solution
As the reaction proceeds, the number of reactants decreases and the number of products increase in a chemical reaction. The number of reactants consumed or the number of products formed depends on the overall rate of the reaction. The rate of formation or the rate of disappearances is equal to the overall rate of the reaction. Depending on the experimental conditions, the rate of reaction changes as the concentration of reactants, pressure in case of gases, temperature, and catalyst.
Complete answer:
Consider a single one-step reaction:
A→B
The rate of reaction = R = rate of disappearance = rate of formation of products
R =−ΔtΔ[A]=ΔtΔ[B]
Where R is the rate of the overall reaction.
Δ[A],Δ[B] , are the concentrations of the reactant and products respectively, Δt will be changing in time.
Factors affecting the rate of reaction:
(i) Concentration of reactants
(ii) Temperature
(iii) Effect of solvent
(iv) Phase and surface area of reactants
(v) Catalyst
Temperature:
The minimum energy required to proceed with a reaction called activation energy. A measure of the average kinetic energy of the particles of substance is the temperature (T) and the temperature increases in a system that causes the rate of reaction to increase. Hence, the rate of reaction R is proportional to the temperature.
In the given curves, option B curve represents in a one-stop reaction that the rate is linearly proportional to temperature.
Hence, the correct answer is option B.
Note:
The ratio of the two rate constants of two temperatures differs by 100C is known as the temperature coefficient of the reaction. The rate of reaction is doubled when every 100C temperature rise. The temperature coefficient is a measure of temperature sensitivity of chemical reaction rates and biological processes.
