Question
Question: Which combination is best explained by the coordinate covalent bond? (A)- \({{H}_{2}}+{{I}_{2}}\) ...
Which combination is best explained by the coordinate covalent bond?
(A)- H2+I2
(B)- Mg+21O2
(C)- Cl + Cl
(D)- H++H2O
Solution
A bond formed by sharing a pair of electrons by two atoms from one atom only is called a coordinate bond or a dative covalent bond. Hydronium ions have two O-H covalent bonds and one O-H coordinate bond which after the formation of O→H+ co-ordinate bond becomes identical to the two O-H covalent bonds. Hence in H3O+ ion all the three bonds are identical.
Complete answer:
-A covalent bond is a kind of 2-center, 2-electron bond in which the two electrons derived are from the same atom.
-This type of bonding is seen in coordination compounds where a metal ion is bonded to ligands.
- In the first option, the combination given is H2+I2 which forms 2HI. The HI molecule exists with a covalent molecule with H and I sharing one electron each.
-In the second option, the combination given is Mg+21O2 which forms MgO. In MgO molecules, oxygen gains two electrons to complete its octet and the bond formed is an ionic bond.
-In the third option, the combination given is Cl + Cl which forms a chlorine molecule. In Cl2 , both atoms share and tightly hold each other’s electrons and form a covalent bond.
-In the fourth option, the combination given is H++H2O which forms H3O+ . The bonding in the hydronium ion is a coolant bond, in which one electron comes from the oxygen and one comes from the hydrogen.
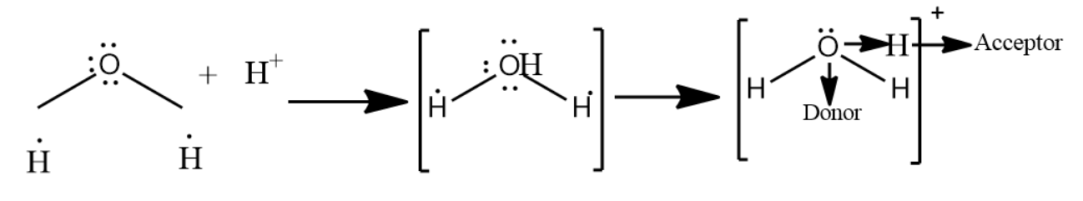
Therefore, the best combination explaining the coordinate bond is the combination of H++H2O
So, the correct answer is “Option D”.
Note: Hydronium is the common name of aqueous cation which is a type of oxonium ion produced by protonation of water. Hydronium ion has a trigonal pyramidal molecular geometry with the oxygen atom at its apex. The H-O-H bond angle is approximate 113∘ .
