Question
Question: Which cell organelle is responsible for secretions?...
Which cell organelle is responsible for secretions?
Solution
Secretion is the ability to deliver vesicles, or packets of varied cell products, to different locations throughout the cell. It also has important functions in tagging vesicles with proteins and sugar molecules, which serve as identifiers for the vesicles so they can be delivered to the proper target.
Complete answer:
Plastids are present in most plant cells and are not present in animal cells.
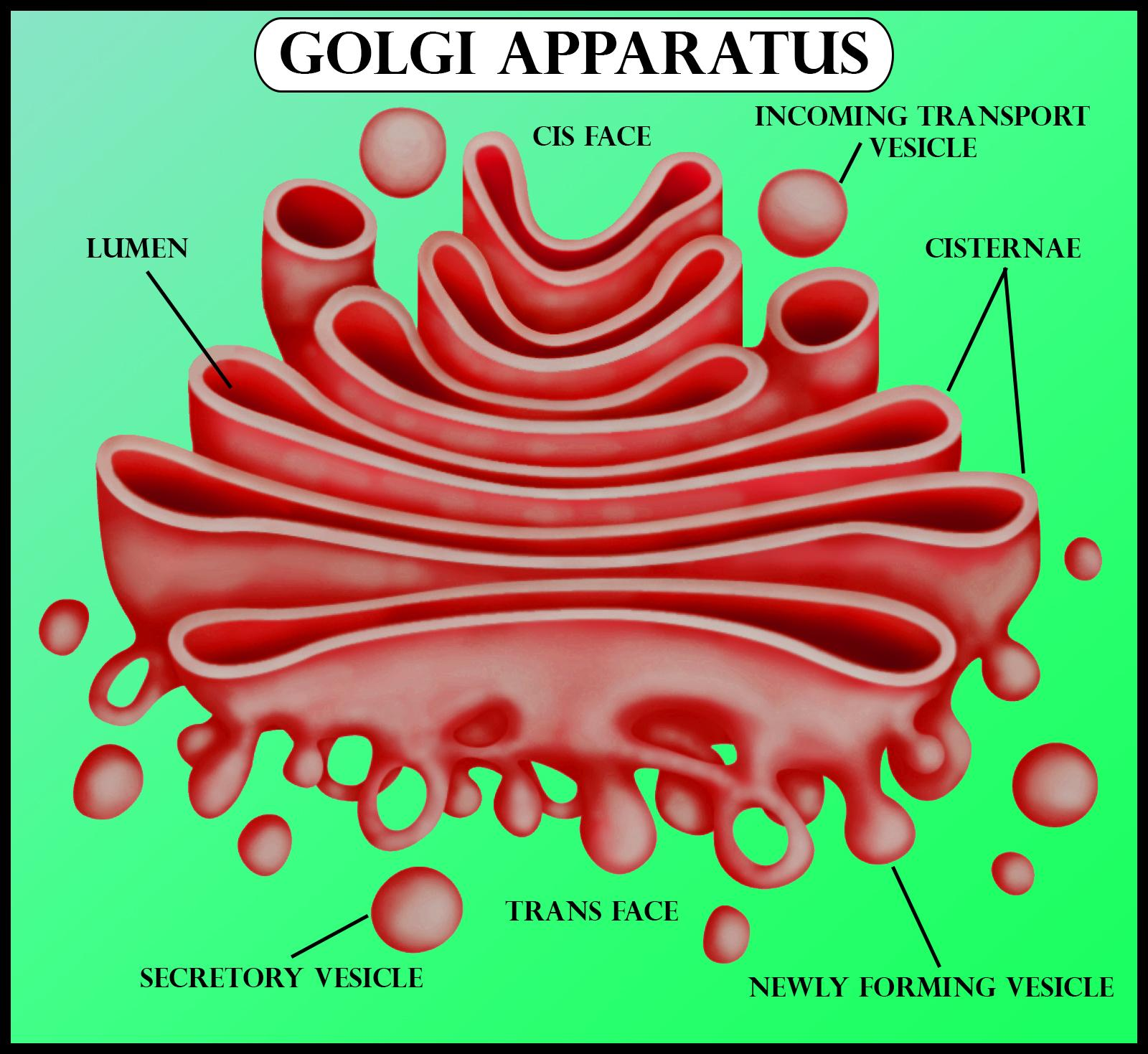
The Golgi body comprises a gathering of film limited, liquid-filled vesicles, vacuoles, and leveled cisternae.
Synthesis and secretion of enzymes, hormones etc.
The formation of the acrosome of sperm.
Endoplasmic reticulum: inside the cells there exists a membrane network closing a fluid-filled lumen which almost fills up the intracellular activity.
Nucleolus may be one or more in no. and is not bounded by any membrane.
Additional information:
There are numerous items that are delivered by eukaryotes, from proteins that can do substance responses to lipid particles that can assemble new cell layers. A few items are intended for the endoplasmic reticulum or the Golgi body itself and travel the other way of most vesicles. While the endoplasmic reticulum delivers the vast majority of the items and bases utilized, it is the Golgi body that is liable for the last introduction and gathering of items. Frequently, the climate must be somewhat not quite the same as that present inside the endoplasmic reticulum to get certain finished results. The numerous sacs of the Golgi body capacity give a wide range of territories in which responses can happen in the most ideal of conditions.
So the correct answer is ‘Golgi apparatus’.
Note:
In secretory cells, or cells that produce a lot of a substance that your body needs, the Golgi body will be exceptionally enormous. Consider the cells in your stomach that discharge acid The acid is delivered by responses inside the endoplasmic reticulum and is changed as it experiences the Golgi body. Once to the trans side of the Golgi body, the acid is bundled during a vesicle and sent towards the cell's surface.