Question
Question: Which \[\beta \]- keto acid shown will not undergo decarboxylation? 
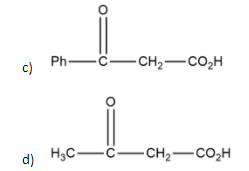
Solution
Keto acids are also called oxo acids. These are organic compounds that contain a carboxylic acid group and a ketone group. There are 3 types of keto acids alpha, beta and gamma keto acids.
Complete step by step answer:
Compounds which contain carboxylic COOHand ketone group C=Opresent in it are known as keto acids or oxo acids. On the basis of attachment of ketone groups these are divided into 3 parts.
α- keto acid in which ketone group is present at alpha carbon atom
β- keto acid in which ketone group is present at beta carbon atom
γ - keto acid in which ketone group is present at gamma carbon atom which can be shown as:
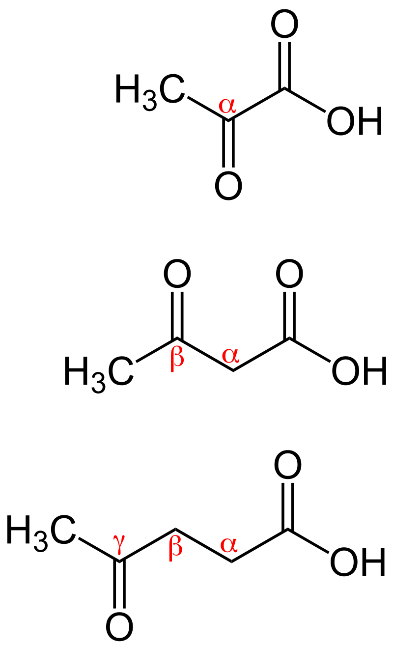
Decarboxylation takes place when carboxylic acids containing a carbonyl group two bonds away (on the βcarbon) are heated and carbon dioxide is lost during this process.
In the case of compound b, \alpha $$$$\beta −keto acid having it's αcarbon at bridged head so it can't undergo tautomerization and it has a fixed hybridisation of sp3 and can't undergo decarboxylation while on the other compounds β position is free so decarboxylation can be occur easily.
Thus, option b is right.
Note: Decarboxylation is the process in which loss of carbon dioxide is there in this process of tautomerization. Tautomerism is the ability of certain organic compounds to react in isomeric structures that differ from each other in the position of a hydrogen atom and a double bond.
