Question
Question: Which are the incorrect statements? A.Frenkel defect is favored in those ionic compounds in which ...
Which are the incorrect statements?
A.Frenkel defect is favored in those ionic compounds in which sizes of cation and anions are almost equal.
B. FeO0.98 Has non stoichiometric metal deficiency defect.
C.Density decreases in case of crystals with Schottky’s defect.
D.NaCl (s) is insulator, silicon is semiconductor, silver is conductor, quartz is piezoelectric crystal.
Solution
To solve this question we need to know about the defects in the crystals. There are various kinds of defects such as Frankel defect, Schottky defect, metal deficiency defect and many more. Moreover, there are different properties of metals. Some of them are conductors, some are insulators while some are semiconductors.
Complete step by step answer:
There are various defects in solids. The point defects explain about the imperfections of solids along with the types of point defects. Basically, there are three types of point defects: Stoichiometric defect, Frenkel defect and Schottky defect. Further, we have vacancy defect and interstitial defect in stoichiometric defect.
Now, in the Frenkel defect, in ionic solids the smaller ion i.e. cation moves out of its place and occupies an intermolecular space. So, in this case, a vacancy is created on its original position and interstitial defect i.e. the atom or molecule occupies the intermolecular spaces in the crystal is experienced at its new position. This defect occurs when cations are smaller in size as compared to anions. Moreover, in case of Schottky defect equal number of cations and anions are missing from the compound. It reduces the density of the substance and the size of cations and anions are the same. The defects are as shown:
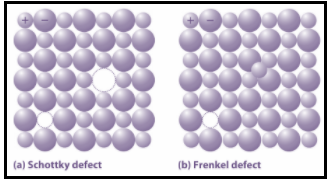
Further, NaCl is an insulator i.e. it does not conduct electricity, silicon is semiconductor, silver is conductor and quartz are piezoelectric crystals. Moreover, FeO0.98 is a non stoichiometric metal deficiency defect. In this defect, the solids have a smaller number of metals relative to the described stoichiometric proportion.
Hence, option A is correct.
Note: There is one more type of non-stoichiometric defect i.e. metal excess defect. It is of two types i.e. due to anionic vacancies and due to presence of extra cations at interstitial sites. The first one occurs due to absence of anions from its original lattice site in crystals and the second one, the cations occupy the interstitial sites in crystals and the same number of electrons go to the neighboring interstitial sites.
