Question
Question: Which are the following pairs of species that have identical shapes? (A) \( NO_{2}^{+} \) and \( \...
Which are the following pairs of species that have identical shapes?
(A) NO2+ and NO2−
(B) PCl5 and BrF5
(C) XeF4 and ICl4−
(D) TeCl4 and XeO4
Solution
Hint : We know that valence shell electron pair repulsion (VSEPR) theory is used to determine the geometry and shape of molecules from the electron pairs surrounding the central atom. The electron pairs may be bonded pairs or lone pairs.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
Valence shell electron-pair repulsion theory (VSEPR theory) enables us to predict the molecular structure, including approximate bond angles around a central atom, of a molecule from an examination of the amount of bonds and lone electron pairs in its Lewis structure. A lone pair of electrons occupy more space than a bonding pair of electrons because lone pair of electron is under the influence of only one nucleus of the central atom, they are expected to occupy more space with a greater electron density than the bond pair electrons which are under the influence of two nuclei. The decreasing order of repulsion is mentioned below
Lone pair − Lone pair repulsion > Lone pair-Bond pair repulsion > Bond pair − bond pair repulsion.
Repulsion forces decrease sharply with increasing interior angle. They are stronger at 90 degree, weak at 120 degree and very weak at 180 degree. Influence of a bonding electron pair decreases with increasing value of electronegativity of an atom forming a molecule. A central atom can be defined as any atom that is bonded to two or more than two other atoms. The first and the most important rule of the VSEPR theory is that the bond angles about a central atom are those that minimize the total repulsion experienced between the Electron pairs in the atom’s valence shell. Multiple bonds behave equivalent to a single electron pair for the purpose of VSEPR bond theory. Thus only option B has identical shapes:
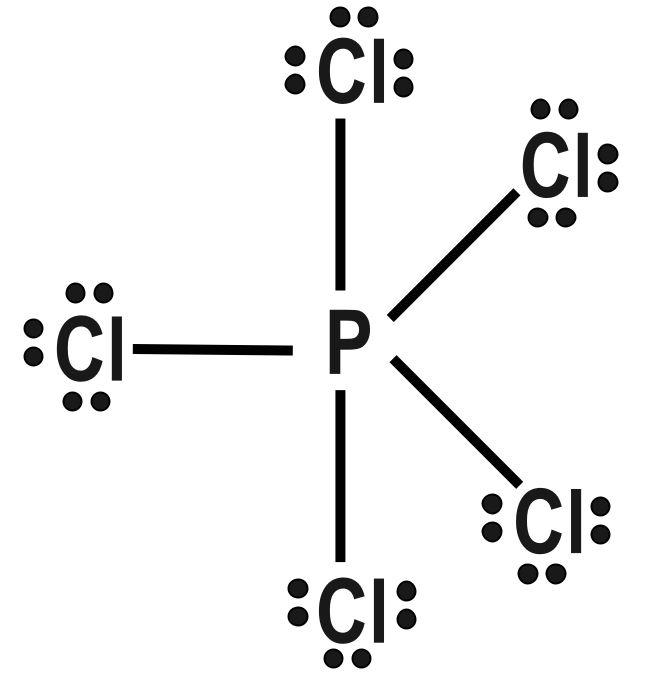
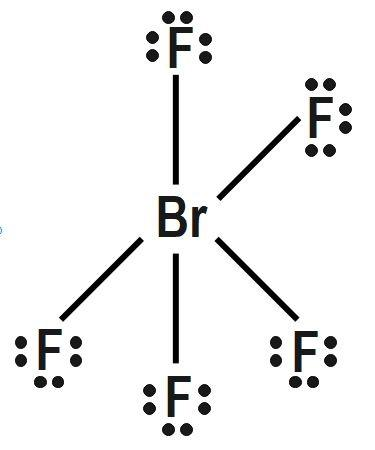
Therefore, correct answer is option B.
Note :
Pauling's big contribution to chemistry was valence bond theory, which combined his knowledge of quantum mechanical theory along with his knowledge of basic chemical facts, like bond lengths and bond strengths and shapes of molecules. Valence bond theory, like Lewis's bonding theory, provides a straightforward model that's useful for predicting and understanding the structures of molecules, especially for chemical science.
