Question
Question: Which among the following glands is situated beneath the brain and whose over secretion produces gia...
Which among the following glands is situated beneath the brain and whose over secretion produces giant size children
A. Pituitary
B. Thyroid
C. Adrenal
D. Pancreas
Solution
The growth hormone is responsible for the normal growth in our body. It is secreted by an endocrine gland. Overproduction and underproduction of growth hormone cause severe abnormalities in children.
Step by step answer: The other name of the pituitary gland is hypophysis. It is a small pea-shaped gland that is located in a bony cavity called sella tursica. It is an example of an endocrine gland and it produces several hormones essential for the normal metabolism of our body. It has two lobes called the anterior pituitary lobe and the posterior pituitary lobe. The posterior pituitary lobe contains hormones that are produced by the hypothalamus.
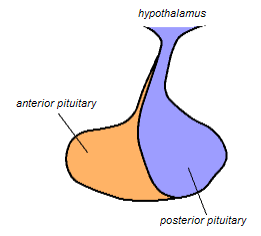
Anterior lobe is called pars distalis and the posterior lobe is called pars nervosa. The middle lobe atrophies during the foetal development. Major hormones secreted by the pituitary gland are growth hormone, thyrotropic hormone, adrenocorticotropic hormone, prolactin, and gonadotropins. Growth hormone is secreted by somatotropic cells present in the pituitary gland. It controls the synthesis and accumulation of proteins in the body which leads to bodybuilding. It also helps for the growth and elongation of bones along with growth of muscles. Abnormal secretion of growth hormones leads to several problems. Decreased growth hormone secretion leads to dwarfism in which the individual is short in stature. Also, the excess secretion of growth hormones from childhood results in a large-sized body, and the condition is called gigantism.
Hence the correct option is A
Note: Hypersecretion of growth hormone in adults also creates problems. The condition is called acromegaly. In these individuals, abnormal elongation of bones and other body parts is seen. Facial bones become enlarged along with disproportionate growth of body parts.
