Question
Question: Which amino acid is achiral? A.Alanine B. Valine C. Proline D. Glycine...
Which amino acid is achiral?
A.Alanine
B. Valine
C. Proline
D. Glycine
Solution
Optical activity of an organic compound depends upon the presence of chiral carbon present in it. A compound consisting of a chiral carbon is said to be optically active.
Complete step by step answer:
Let us get to know about chiral carbon first:
- If all the four valencies of carbon are satisfied by 4 different groups the carbon is chiral carbon or asymmetric carbon. Presence of chiral carbon never ensures the molecule is optically active.
Compounds with one chiral carbon are always chiral. While compounds containing more than one chiral carbon may or may not be chiral.
Whereas achiral carbon is a carbon which is optically inactive and in which there are at least 2 same substituents are present.
Any molecule is optically active if
(a) it is non-superimposable on its mirror image.
(b) does not contain any element of symmetry
- Elements of symmetry offer a simple device to decide whether a molecule is chiral or achiral, i.e., whether the molecule is superimposable or non-superimposable on its mirror image. When a molecule lacks all elements of symmetry it is chiral.
(1) Plane of symmetry : Any imaginary plane which divides the full molecule into two halves which are mirror images of each other.
(ii) Centre of inversion : Any imaginary point, through which when inversion will be carried out it will repeat equivalent configuration.
(iii) Alternating axis of symmetry (S): A molecule is said to inherit an alternating axis of symmetry as it gets rotated via an angle of n360 about the axis and then reflected in a plane perpendicular to the axis, molecule comes to its equivalent form.
- Enantiomers: Molecules which are mirror images of each other becoming non superimposable are called enantiomers.
(i) Enantiomers have the same physical properties but differ in the optical rotation which is equal in magnitude but direction is opposite.
(ii) Enantiomers have the same chemical behaviour towards the molecules which are optically inactive, but they have different chemical behaviour towards the molecules which are optically active.
Diastereomers: Stereoisomers which do not entertain as mirror images of one other are said to be diastereomers. Diastereomers have different physical as well as chemical properties.
Some examples of optically active molecules are ascorbic acid , all amino acids , tartaric acid etc.
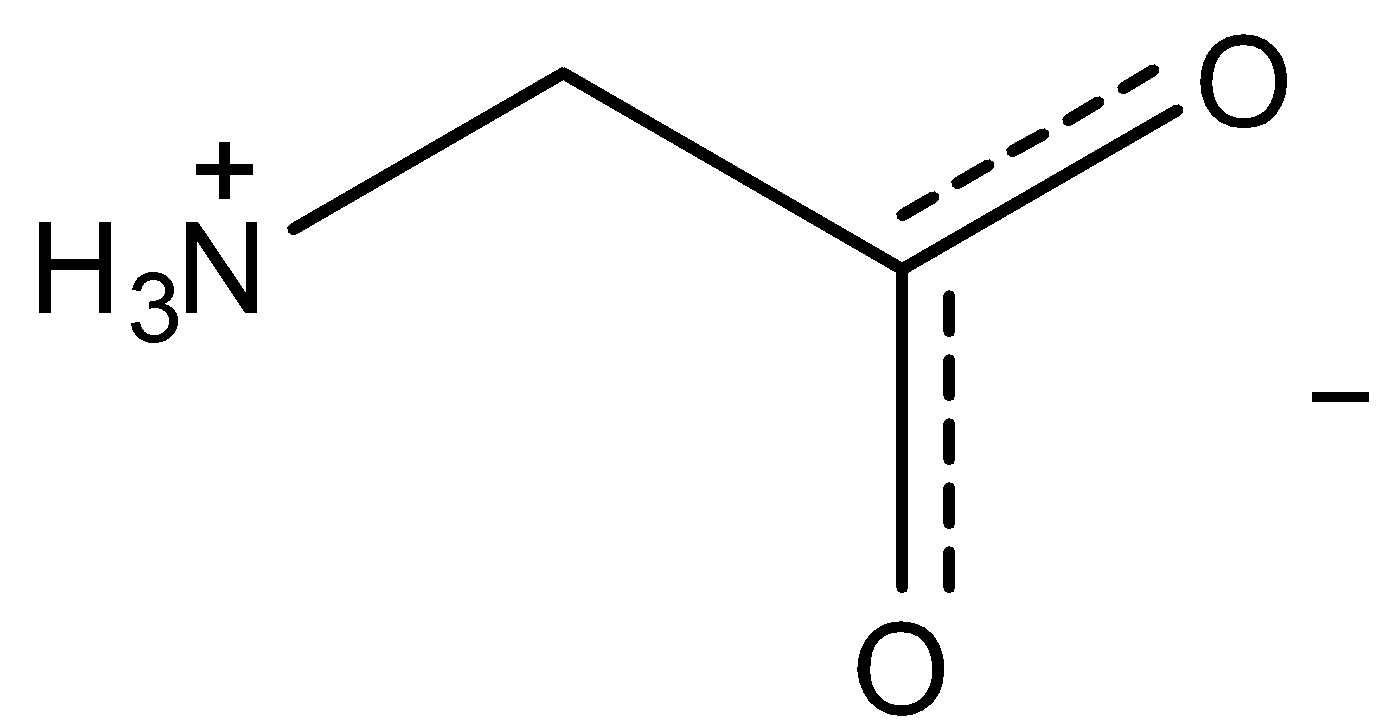
Now among the following options only glycine has achiral carbon present in it .
So, the correct answer is “Option D”.
Note: Racemic Mixture:
1:1 molar mixture of dextro and laevo forms of the same enantiomeric pair is optically inactive because the optical rotation due to dextro form is compensated by the optical rotation due to laevo form. It is the case of external compensation.
