Question
Question: Where will the image form when we place an object, on the principal axis of a concave mirror at a po...
Where will the image form when we place an object, on the principal axis of a concave mirror at a point between focus and centre of curvature?
Solution
A concave mirror is a type of spherical mirror. In a concave mirror, the reflecting surface is curved inwards. Concave mirrors are converging mirrors. Hence they can be used to focus light. The type of image formed by the concave mirror varies depending on the distance between the object and mirror.
Complete step by step solution:
Spherical mirrors are reflecting surfaces that are part of a sphere. If the inner surface is the reflecting surface, then the mirror is concave. If the outer surface is reflecting then it is a convex mirror.
The centre of curvature of a spherical mirror is the centre of the sphere of which the mirror is a part.
The principle axis of a mirror is a straight line passing through the pole (P) and the centre of curvature (C) .
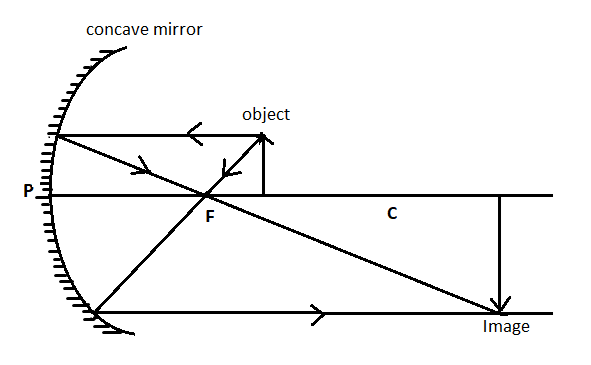
As shown in the ray diagram, the object is placed between the centre of curvature and the focal point.
The image is formed beyond the centre of curvature. The image will be real, enlarged, and inverted.
The image is formed beyond the centre of curvature.
Note: The light rays starting from a point on the object are reflected by the mirror and finally meet at a point to form an image. To construct the image any two of the following rays can be taken.
1. The ray coming from the object and parallel to the principal axis, after reflection passes through the principal focus of the mirror in the case of a concave mirror (and appears to diverge from the focus in the case of a convex mirror)
2. The ray coming from the object and directed towards the centre of curvature retraces its path after reflection.
3. The ray coming from the object and directed towards the principal focus goes parallel to the principal after reflection.
4. The ray falling at the pole reflects with an angle of reflection equal to the angle of incidence.
