Question
Question: When the resistance of a conductor increases, the current will ________ provided the same potential ...
When the resistance of a conductor increases, the current will ________ provided the same potential difference is applied across it.
A. Increase
B. Decrease
C. Remain the same
D. Become double
Solution
To deduce relation between current, voltage and resistance, use Kirchhoff’s law. Resistance is inversely proportional to the current passing through the conductor. When the resistance of a conductor increases, collision of electrons increases hence it opposes current to flow through it.
Complete step-by-step answer :
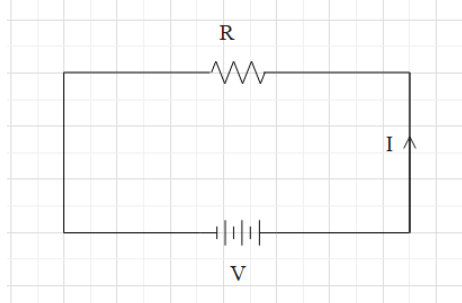
To answer this question, first we should know the relation between resistances, voltage, and current.
Relation between current, resistance and voltage is given by ohm's law and Kirchhoff’s law.
But ohm's law has limitations. So we will go with Kirchhoff’s law,
According to Kirchhoff’s law, it states that sum of product current and resistance is equal to the sum of potential difference applied across circuits.
V=IR
where,
I= current flowing through circuit
V= voltage applied across circuit
R= resistance across circuit
We can also write this equation as, if voltage applied is constant.
I∝R1
So, when the resistance of a conductor increases, the current will decrease.
Why it is so, we will see in further.
The atoms are tightly bound and current is carried by negatively charged electrons. When no external potential difference is applied, the electrons move in random direction and collide with atoms. The average number of electrons crossing any section in One Direction is equal to the average number of electrons crossing their section in the opposite direction in a given time. Thus, there is no net Of electrons through any section of the conductors. Hence, there is no electric current.
When potential difference is applied across conductors in the electric field is set up inside the conductor. The negatively charged electrons move in direction opposite to this field. There is a continuous flow of electrons across the cross section of the conductor. Atoms of any material are always in a state of vibration because of thermal energy. While moving, electrons continuously collide with vibrating atoms and their motion is opposed and electron remove with constant velocity called drifted velocity. This opposition gives rise to the resistance of conductors.
Hence the correct answer is (B).
Note : Amplitude of atomic vibration depends on temperature of conductor. At higher temperatures, atoms vibrate with large amplitude and hence motion of electrons is largely opposed due to more frequent collision. This increases resistance of conductor and decreases this current flow in the conductor.
