Question
Question: When EDTA solution is added to \[{\text{M}}{{\text{g}}^{{\text{2 + }}}}\] ion solution, then which o...
When EDTA solution is added to Mg2 + ion solution, then which of the following statements is not true?
A) Four coordinate sites of Mg2 + - are occupied by EDTA and remaining two sites are occupied by water molecules.
B) All six coordinate sites of Mg2 + are occupied.
C) pH of the solution is decreased.
D) Colourless [Mg - EDTA]2− is formed.
Solution
The coordination number of octahedral complexes is 6. Usually, a hexadentate ligand forms six bonds with central metal cation. When hydrogen ion concentration changes due to complex formation reactions, the pH of the solution also changes.
Complete answer:
The full name of EDTA is ethylene diamine tetraacetic acid. The structure of EDTA is shown below:
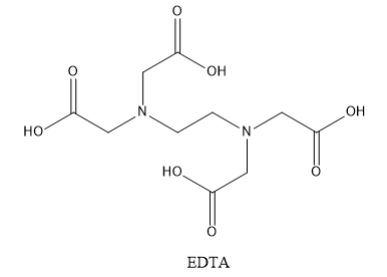
EDTA contains six donor atoms. These include two nitrogen atoms and 4 oxygen atoms. Thus, EDTA is a hexadentate ligand.
When you add EDTA solution to Mg2 + ion solution, you will get the following reaction.
Mg2 + + [H2EDTA]2−→[Mg(EDTA)]2− + 2H +
Four coordinate sites of Mg2 + - are occupied by forming bonds with four oxygen atoms of EDTA and remaining two sites are occupied by forming bonds with two nitrogen atoms of EDTA. Thus, all six coordinate sites of Mg2 + are occupied.
When EDTA reacts with Mg2 + ions, it produces protons. This increases the hydrogen ion concentration and decreases the pH of the solution.
The colourless [Mg - EDTA]2− complex is formed during the reaction.
Thus, the option (A) represents a false statement.
Note: The hexadentate EDTA ligand is a chelating ligand. It forms highly stable metal chelates. Hence, EDTA is used in the titration to detect the presence of certain metal cations.
