Question
Question: When bromoethane is treated with potassium sulfide, the main product formed is: A) Ethanethiol ...
When bromoethane is treated with potassium sulfide, the main product formed is:
A) Ethanethiol
B) Ethanol
C) Mustard gas
C)Thio ethyl ethane
Solution
When a mixture of haloalkanes is heated with the aqueous-alcoholic sodium or potassium sulfides, thioethers are formed. The sulfide acts as a nucleophile and its attack on the haloalkane.
Complete answer:
In haloalkanes, the carbon is bonded to the halogen atom (X=F,Cl,Br,I) which is more electronegative than carbon. The C-Xbond is polar. As a result, the carbon acquires the partial positive charge and halogen gets a partial negative charge. This polar nature makes them highly reactive molecules. The positive charge on the carbon atom is attacked by the nucleophile. Some of the examples of nucleophiles are OH-,CN-,NH3,S2-,etc.
The alkyl halide R-X was treated with sodium sulfide Na2Sor potassium sulfideK2S. The reaction of alkyl halide is converted into the thioether or sulfidesR-S-R.
The general reaction of the formation of thioether is
2RX+Na2SC2H5OH/H2O !!Δ!! R-S-R+2NaX
Let's take an example of bromoethane (CH3-CH2-Br) treated with potassium sulfide K2S
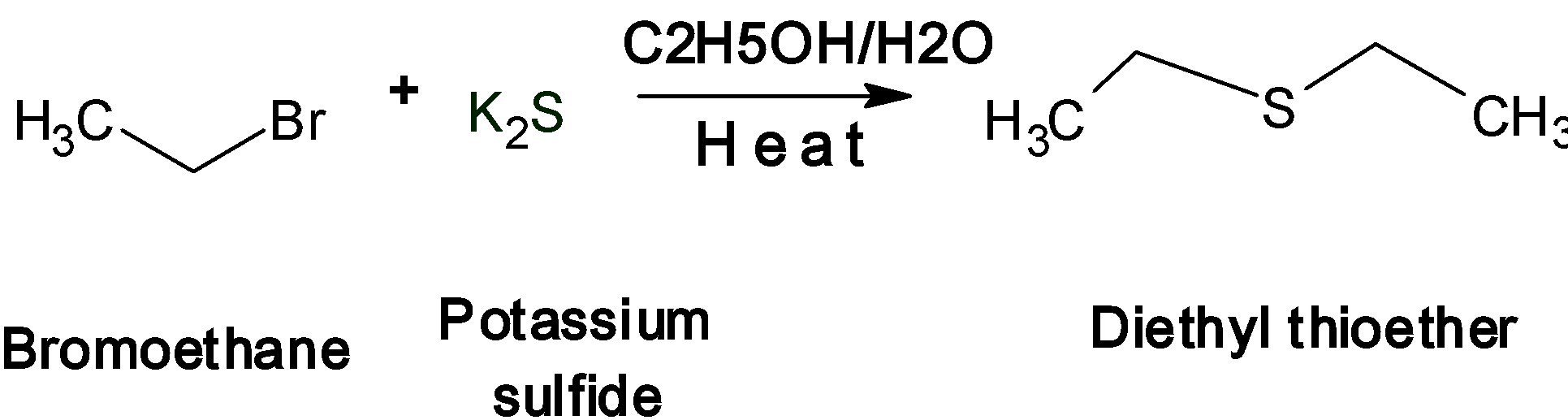
Sulfur analogs of ether are named as the thioether. This is one of the important nucleophilic substitution reactions of halogens. Here sulfide ion S2-acts as a nucleophile. During the reaction, the two bromoethane molecules react with the potassium or sodium sulfide. The two Br-ions from the bromoethane are removed as the two molecules of theHBr. The sulfide ion S2-acts as a nucleophile and attacks simultaneously on the ethyl cation CH3-CH2+to form a thioether.
The dimethyl thioether is also called thio ethyl ethane.
Hence, (D) is the correct option.
Additional information:
The sulfur analogs of ethers are called as the thioethers or sulfides as in alkyl ether nomenclature.
The general nomenclature for thioether is Alkyl thioether or Alkyl sulfide.
Note:
The sulfide ion S2- is an electron-rich species therefore it attacks the electron-deficient species like carbocation. Pay extra attention to the flow of the electron.
