Question
Question: When benzene-1,3-dicarbaldehyde reacts with 50% of \(NaOH\), the possible products formed is/are: ...
When benzene-1,3-dicarbaldehyde reacts with 50% of NaOH, the possible products formed is/are:
A. 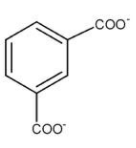
B. 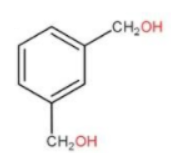
C. 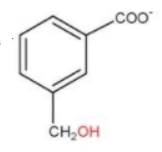
D. 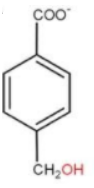
Solution
It is a Cannizzaro reaction, when a self oxidation reduction reaction in which aldehydes that do not have any α-hydrogen atom undergo disproportionation reaction (i.e., self-redox reaction) in the presence of 50% aqueous or ethanolic solution of alkali in which one of the molecules being reduced to alcohol and other being oxidised to the salt of the corresponding acid.
Complete answer:
We are given benzene-1,3-dialdehyde which has a structure like this.
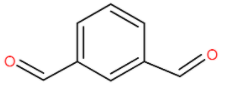
At both α-position of the compound that is 1 and 3, we don’t have a hydrogen atom. So the condition for Cannizzaro reaction is true and we have a 50% of NaOH. Hence the Cannizzaro reaction will occur here. Also since there are two carbonyl groups it undergoes intramolecular Cannizzaro reaction.
As we know that it is a disproportionation reaction, both oxidation and reduction happen in the molecule. When the carbonyl compound is attached to 1st and 3rd position of the benzene it gets oxidised to form −COO−. So we understood that at position 1 and 3 at some point of time we will have −COO− attached, hence option (a) is a possible product.
Also when benzene-1,3-dialdehyde gets reduced to form alcohols at position 1 and 3 we get −CH2OH. Hence option (b) is also a possible product.
And on the intermediate of this, it may also occur at some point of time one −COO− and one −CH2OH is formed. Therefore, option (c) is also a possible product.
Now, coming to option(d) we can see that the position of −COO− and −CH2OHare at 1 and 4 respectively, which is never going to happen as the carbonyl group are present and 1 and 3 position of the compound. Hence this product never forms.
**Hence, options A,B and C are correct.
Note:**
In the presence of α-hydrogen the reaction occurred is known as aldol condensation. In this reaction, two molecules of aldehydes or ketones having α-hydrogen condense together in presence of a base like NaOH to form β-hydroxy aldehyde or β-hydroxy ketone respectively which are collectively known as aldol.
