Question
Question: When acetamide is treated with \[B{r_2}\] and caustic soda, the product formed is: A.N-bromamide ...
When acetamide is treated with Br2 and caustic soda, the product formed is:
A.N-bromamide
B.bromoacetic acid
C.methanamine
D.ethanamine
Solution
The reaction of amides with bromine in the presence of caustic soda gives the following primary amines. And if the reactant is acetamide then it is known as Hofmann’s bromamide degradation which gives the primary amine-containing one carbonless.
Complete step by step answer:
Let us understand the reaction in a stepwise manner:
Step 1: We know that the caustic soda (NaOH) is a strong base so the hydroxide ion from the caustic soda attacks the acetamide leading to the deprotonation of acetamide and formation of the anion of acetamide. Let us see the structure of anion of acetamide:
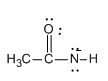
Step 2: Now the anion formed attacks on the bromine molecule leading to the formation of N-bromamide. Let us see the structure of N- bromamide.
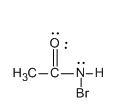
Step 3: Now the deprotonation of N-bromamide ion takes place and the formation of N-bromamide anion occurs. Let us see the structure of N-bromamide anion.
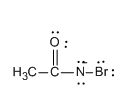
Step 4: Now the N-bromamide anion shows rearrangement and the result of rearrangement is that the methyl group joins nitrogen instead of the carbonyl carbon group which leads to the formation of isocyanate. The isocyanate then leads to the formation of methanamine.
Let us see the structure of methanamine.
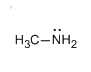
The reaction of acetamide with bromine in the presence of caustic soda can also be represented as:
CH3 - CO - NH2 + Br2 + 4NaOH343KCH3 - NH2 + 2NaBr + Na2CO3
Therefore, we can conclude that the correct answer to this question is option C.
Note:
The product formed here is always one carbon less than that of reactant so ethanamine cannot be possible. And N-bromamide is the intermediate of this reaction so it cannot be the final product.
