Question
Question: When a fork is lensed through lenses A and B one by one , it appears as shown in the diagrams. What ...
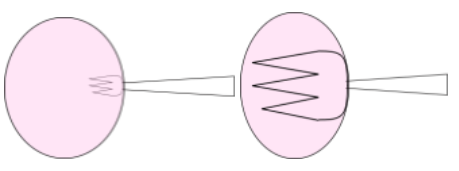
When a fork is lensed through lenses A and B one by one , it appears as shown in the diagrams. What is the nature of (i) lens A and (ii) lens B? Give reason for your answer.
Solution
In common there are two types of lens when is convex lens and another is concave lens As we know that image formed by concave lens is it diminished and virtual and the image formed by convex lens may be magnified or in small size But in concave lens images always small in size then object
Complete solution:
Step 1
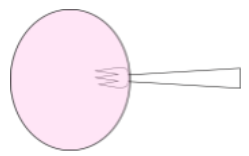
As we can see from the diagram in image A The fork looks smaller than it's real size so we can guess it is a concave lens.
We can understood this by seeing the diagram which is given below:
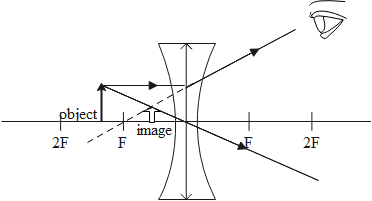
When the object placed near to the concave lens then the image formed in the same side of the lens but in small size When we see object from another side of lens it seems small in size as you can see in above figure
Step 2
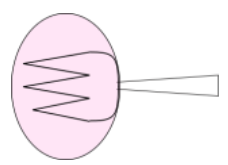
And in diagram B the fork seems to bigger then it's real size means the image formed by the lens his bigger than the original size of fork this is only possible in a particular situation in convex lens
Ray diagram for convex lens given below for this condition:
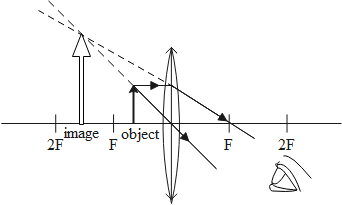
When the object placed near to the optical centre of lens then only the image formed by the convex lens is larger than the object and formed in the same side of the lens this image is also a virtual image when we see from another side of lens it seems a bigger object image as shown in diagram B.
Note: We use here the Ray diagram of concave lens and convex lens to form the image there are two rules used for image formation by the lens which is:
1. When a Ray comes parallel to the principal axis then after refraction from lens it goes to the focus or seems to come from the focus:
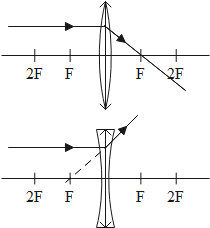
2. When a Ray incident at the optical centre of lens then it will pass through the lens without deflect their path as shown:
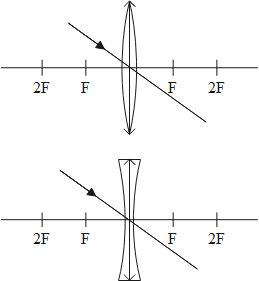
By using these to rule we make the required Ray diagram for lenses.
