Question
Question: Wheat is meant by peptide linkage and biocatalysts?...
Wheat is meant by peptide linkage and biocatalysts?
Solution
peptide linkages are one type of chemical bond which are formed during the polymerisation of amino acid (the building block or monomer of protein).
Catalysts are substances which alter the rate of a chemical reaction without itself being chemically changed.
Complete answer:
Proteins are the polymers of α-amino acid and they are connected to each other by peptide bond or peptide linkage. Chemically, peptide linkage is an amide formed during the condensation polymerisation of amino acids. A peptide linkage is formed in between the -COOH group of one amino acid and -NH2 group of other amino acid.
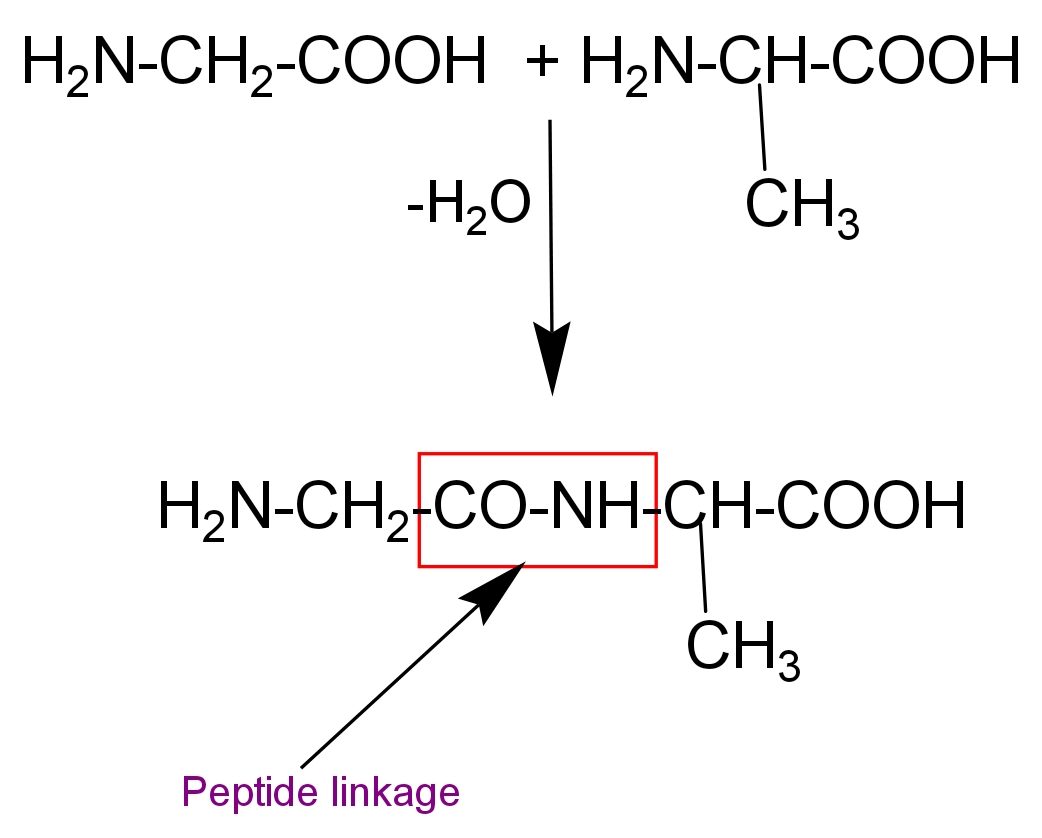
The reaction between two molecules of similar or different amino acids occurs through the combination of the amino group of one molecule with the carboxyl group of the other. This results in the elimination of water molecules and results in formation of a peptide bond (-CO-NH-).
Biocatalysts are enzymes that catalyse the biological reaction within a living organism. These are protein molecules produced in living cells, and each biocatalyst is specific to certain biochemical reactions. They operate only within a narrow range of temperature and pH. Protease and amylase is the enzyme (biocatalyst) which catalyses the breakdown of protein and carbohydrates in the human intestine respectively.
Note:
All the biocatalyst is protein but all the proteins are not biocatalyst.
Peptide bond is a type of covalent bond. Peptide is classified into di, tri, and other polypeptides depending upon the number of amino acids combined.
Biological detergents contain lipase, amylases that catalyse breakdown of stains such as sweat, blood and other food strains.
