Question
Question: What you know about particle theory, explain how oxygen diffuses from an air sac into the blood....
What you know about particle theory, explain how oxygen diffuses from an air sac into the blood.
Solution
The particle theory states that the small particles are in continuous motion state. This motion is dependent on the kinetic energy and the relationship with other particles. In the case of our body physiology, the movement of liquids takes place by the process of osmosis and gases through diffusion. This movement is dependent on the concentration gradient.
Complete answer:
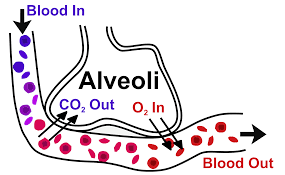
The gaseous exchange is a very important physiological process needed for generating ATP in our body. Lungs are the respiratory organs that help in inhaling the oxygen-rich air and exhaling the carbon dioxide-rich air. The structural and functional unit of the lungs is the alveoli which are the air sacs where the whole of the gaseous exchange takes place between these sacs and the blood. The air sacs are rich in oxygen which is well connected with the capillaries that contain the carbon dioxide-rich blood. The walls of the alveoli are very thin which allows the movement of the gases.
There exist a concentration difference of carbon dioxide and oxygen inside the alveoli and capillaries due to which the diffusion of the two gases takes place. The carbon dioxide moves from the blood to the alveoli sac and the oxygen moves from the sacs to the blood. Thus, diffusion can be defined as the movement of the molecules from the region of higher concentration to the region of lower concentration.
The diagram below shows the diffusion of carbon dioxide and oxygen from the alveoli sacs to the capillaries.
Note: Osmosis is the process that is involved in the movement of the solvent particles across the semi-permeable membrane. They are also guided by the concentration that is from the higher solvent concentration to the lower solvent concentration. Uptake of water by the root hairs is possible due to osmosis.
