Question
Question: What would be the expected product of the reaction of propyne within \({{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\text{...
What would be the expected product of the reaction of propyne within H2O if the mechanism of this reaction is analogous to that of propene?
(A) 2-bromopropane
(B) Bromoacetone
(C) 2-bromo-2-propanol
(D) Bromoprophenol
Solution
The alkyne is triply bonded carbon atom compounds. Here, the electrophile is added to the triple bonded carbon. Since, the electrophile is added across the triple bond we can say it’s a simple electrophilic addition reaction. The product obtained has an acidic proton which favours the continuous interconversions from one isomer to another at the hydroxyl group.
Complete step by step answer:
The alkyne undergoes the attack of bromine molecules followed by the treatment of water. This leads to the formation of halo ketones.
The reaction involves the following steps:
Step 1) The bromine molecule attacks on the triple bond of the propyne. The bromine molecules break down into the electrophile and nucleophile as shown below:
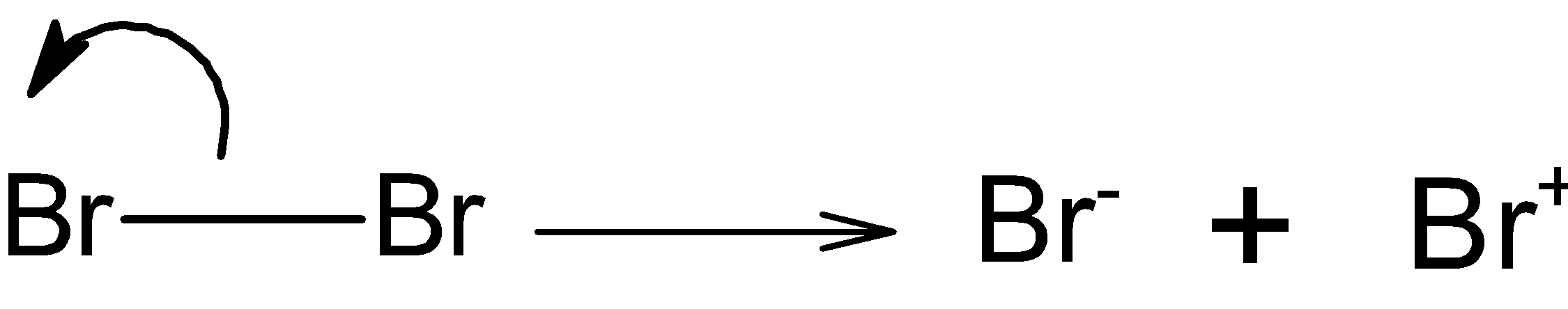
The positively charged bromine attacks on the triple bond.
Step 2) In the next step, the hydroxyl group of the water attack as a nucleophile on the carbocation formed at the carbon atom. This leads to the formation of an alcohol compound.
Step 3) In the next step the enol form of the compound is converted itself into the keto form. This is called the keto-enol tautomerism.The double bond alcohol is converted to the ketone.
When the alkene undergoes the treatment of bromine in water, the double bond is broken, and carbons are now bonded to the bromine and hydroxyl group.
In alkyne, the adjacent carbon atom still holds the double bond, hence undergoes the Tautomerism.
Here, we get the bromoacetone as the product.
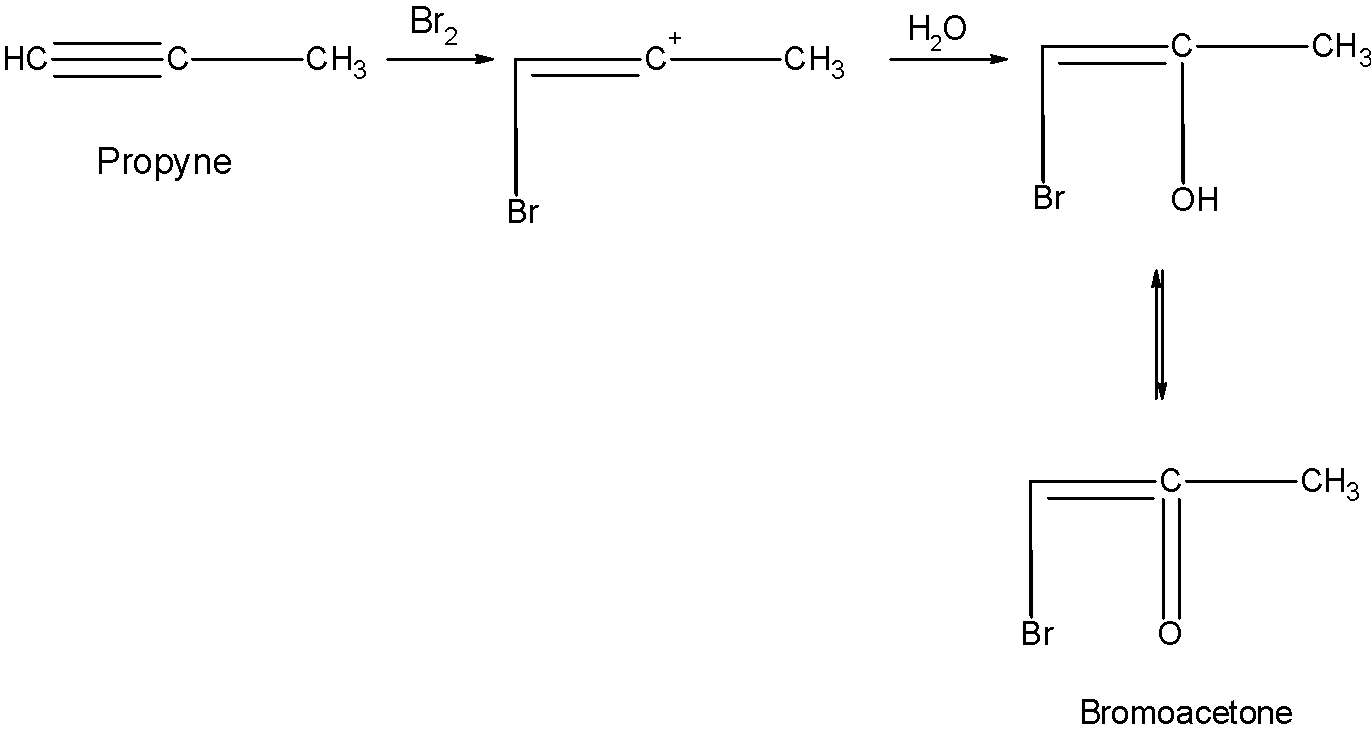
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Additional Information:
Due to the migration of a proton, structural isomers of an organic compound in dynamic equilibrium are called tautomers. One of the important types of tautomerization is keto-enol tautomerization. In our question also, the hydrogen from the alcohol group will migrate to the adjacent carbon and thus forms a new carbon-oxygen double bond keto form. In most of the cases, the keto form is more stable than the enol form.
Note: Tautomerism is a key to obtain the product bromoacetone. Note that the triple bonded carbon has two pi bonds and a sigma bond. Due to high electronegativity, it always undergoes the electrophilic addition reaction. The bromine may be misleading. In most reactions it acts as a nucleophile, but here it acts as an electrophile to give the desired product.
