Question
Question: what will be the product for the given reaction? 
Solution
Dihydroxylation of alkenes can be dihydroxylated by two different stereochemical ways which are anti- dihydroxylation or syn- dihydroxylation. The anti-dihydroxylation mechanism follows the opening of epoxides and potassium permanganate or osmium tetroxide will produce syn-dihydroxylation products. This reaction can also be a two-step process as osmium tetroxide in pyridine solution followed by sodium thiosulfate.
Complete step by step solution:
Syn dihydroxylation: Oxidation of alkenes through Osmium tetroxide to give through syn addition. A vicinal diol is a compound with two –OH groups on adjacent carbons is glycol. Glycols are obtained by reaction with osmium tetroxide in pyridine solution followed by sodium thiosulfate (NaHCO3). The metallic intermediate may be isolated in the osmium reaction and both reactions appear to proceed with the same mechanism.
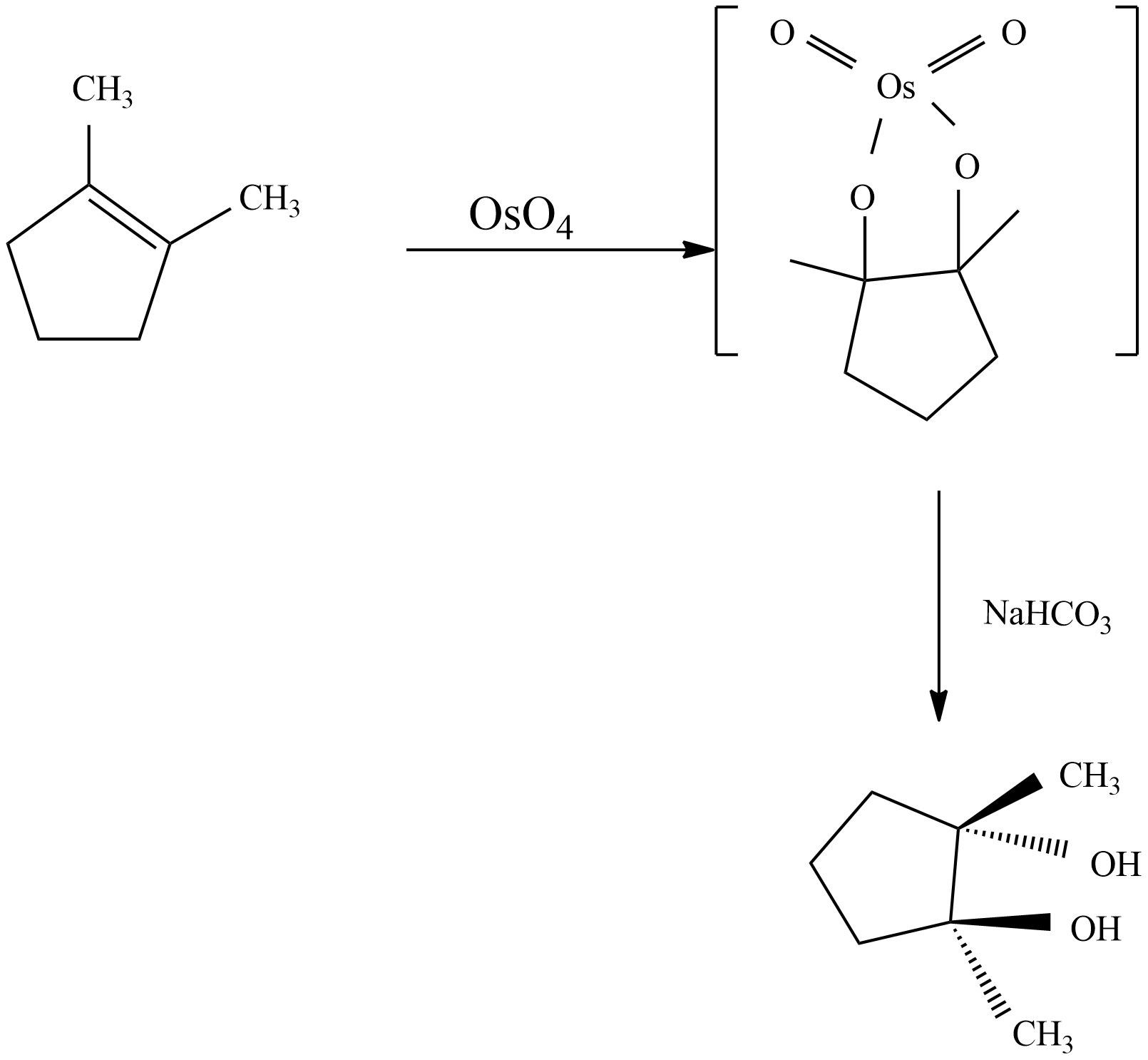
From the mechanism, observed that syn-stereoselectivity in the bonding oxygen and not an issue with region selectivity. The reaction with Osmium tetroxide is a concerted process which has a cyclic intermediate with no rearrangement of vicinal syn dihydroxylation of an alkene. When 1, 2-dimethyl cyclopentene reacts with OsO4 , glycol product will form with stereocenters and the product is option C which is a Meso product from cis-1, 2-dimethyl-cyclopentene.
Note: Syn-hydroxylation of alkenes forms epoxides may be cleared by aqueous acid to give glycols. In contrast to the syn-stereoselectivity of this method is the anti-hydroxylation of the double bond. The given equation is illustrated for a cis-disubstituted epoxide and this hydration of an epoxide does not change the oxidation state of atoms or groups.
