Question
Question: What will be the product for the following reaction \({\text{Ph}} - {\text{C}} \equiv {\text{C}} -...
What will be the product for the following reaction
Ph−C≡C−CH3→Hg2+/H + A
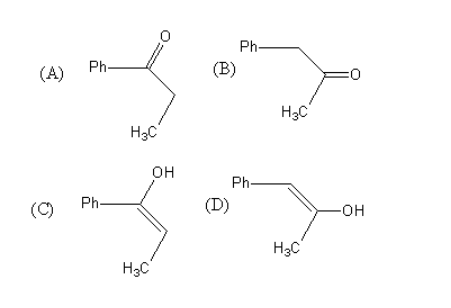
Solution
The alkene and alkyne work as nucleophile and attacks on acid forming a cation. The reagent H2SO4/HgSO4 cause mercuration and demercuration. This reagent breaks the triple bond of alkyne and gets attached. The hydrolysis of the triple bond gives carbonyl as a product.
Complete Step by step answer: The IUPAC name of Ph−C≡C−CH3 is 1− propenyl benzene.
First the mercury attacks on the reactant 1− propynyl benzene and form a cyclic structure. Then water attacks on this cyclic structure forming a mercury cation. Then by the removal of hydride alcohol forms.
The enol can be converted into keto form by keto-enol tautomerism. The oxygen atom of the ketone attacks on the acid and gets protonated and the diacation of mercury removes. The enol form again converts into keto form by keto-enol tautomerism.
The mechanism of the reaction of 1− propenyl benzene with mercuric ion and acid is as follows:
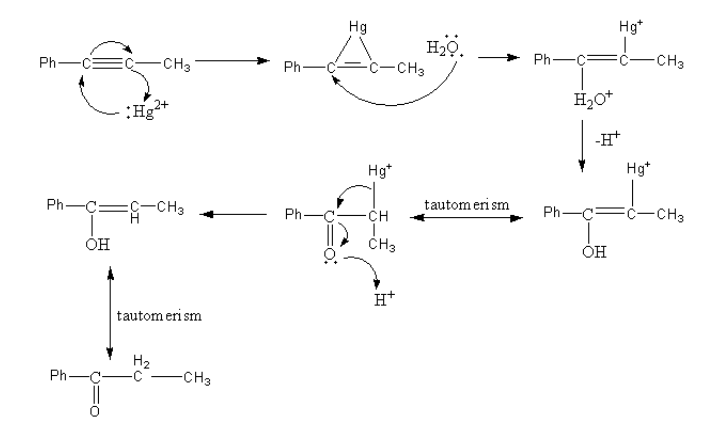
So, the product of the reaction of 1− propenyl benzene with mercuric ion and acid is 1− phenyl prop −1−en−1− on (Option-C) which converts into propiophenone (option-A). So, the main product of the reaction is 1-propenyl benzene.
Therefore, option (A), is correct.
Note: In this reaction, mercury attaches with the reactant in between the reaction mechanism and then removes so, the reaction is known as oxymercuration demercuration. In the case of a symmetrical alkyne, water in the second step can attack from any side, so the ring can open from any side. But in the case of an asymmetrical alkyne, the water attacks from the more nucleophilic side. The Methyl group shows the +I effect and the phenyl ring shows the +M effect so, the carbon attached with the phenyl ring is more nucleophilic.
