Question
Question: What will be the order of reactivity of the following carbonyl compounds with Grignard’s reagent? ...
What will be the order of reactivity of the following carbonyl compounds with Grignard’s reagent?
I. 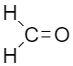
II.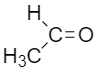
III.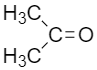
IV.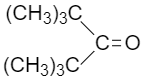
A. I > II > III > IV
B. IV > III > II > I
C. II > I > IV > III
D. III > II > I > IV
Solution
With the increase in the alkyl group, the order of reactivity decreases. Carbonyl carbon contains a carbon atom attached to an oxygen atom by a double bond.
Grignard reaction is a type of coupling reaction and the Grignard reaction was discovered by Francois Auguste Victor Grignard.
Complete answer:
A polar carbon-magnesium bond is present in the Grignard reagent, the carbon atom carries a partial negative charge and the metal carries a partial positive charge. As in the Grignard reagent, the carbon atom has a partial negative charge, it bears a resemblance to a carbanion and reacts with electrophilic centers.
The less bulky R –group has a high rate of reaction towards the Grignard reagent. Steric hindrance of carbonyl compound is responsible for the order of reactivity of nucleophile towards the nucleophilic substitution reaction. With the increase in the alkyl group, carbonyl becomes a weak electrophile, and the order of reactivity decreases.
Formaldehyde is least bulky as compared to the other options as the carbonyl group is attached to hydrogen, In the case of Acetaldehyde, the carbonyl group is attached to hydrogen on one side and an R group on another side so acetaldehyde has a bulky group present and the rate of reaction with Grignard’s reagent for acetaldehyde is low as compared to formaldehyde.
Option IV (CH3)3C(CO)C(CH3)3 shows the least reactivity towards Grignard’s reagent because the more number of CH3 group decreases the positive charge on carbonyl carbon by +I effect. The nucleophilic attack is favorable with a more positive charge and less hindrance at carbonyl carbon.
There the correct answer is option A.
Note:
The order of Reactivity of alkyl halide with Grignard reagent is RI>RBr>RCl. Greater will be the reactivity if the bond energy is low, with the decrease in size of halogen nuclear attraction towards shared electron pair increases (i.e. becomes strong bond) then there is an increase in bond energy that decreases reactivity.
