Question
Question: What will be the compound C in the following reaction: \[{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}} - {\tex...
What will be the compound C in the following reaction:
CH3−C≡CHNa/liq.NH3One equib.ACH3−IBH2/Pd−CaCO3C
Compound ‘C’ is:
A) Trans-but-2-ene
B) Cis-but-2-ene
C) Mixture of cis and trans-but-2-ene
D) Butyne-2
Solution
Initially we are given a compound which is prop-1-yne. Prop-1-yne reacts with sodium metal in liquid ammonia and gets deprotonated. This deprotonated product then reacts with methyl iodide and results in formation of a symmetrical alkyne. The symmetrical alkyne undergoes hydrogenation and forms an alkene.
Complete solution:
We are given a reaction sequence as follows:
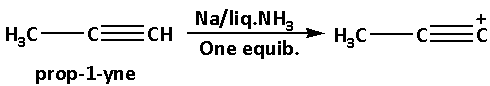
CH3−C≡CHNa/liq.NH3One equib.ACH3−IBH2/Pd−CaCO3C
Initially we have prop-1-yne. Prop-1-yne reacts with sodium metal in liquid ammonia and gives product B.
Prop-1-yne reacts with sodium metal in liquid ammonia and produces a deprotonated product. In this reaction, a proton i.e. one hydrogen atom gets eliminated from prop-1-yne.
The reaction of prop-1-yne with sodium metal in liquid ammonia is as follows:
The deprotonated product reacts with methyl iodide and produces but-2-yne. In this reaction, the methyl group (−CH3) gets attached to the positively charged carbon atom.
The reaction is as follows:
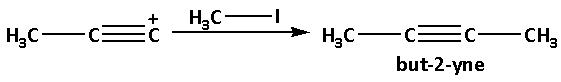
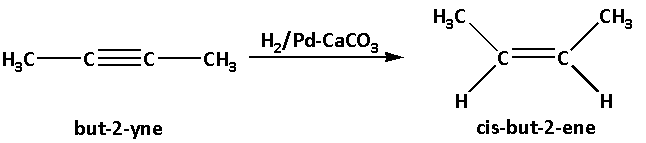
But-2-yne then reacts and undergoes hydrogenation i.e. but-2-yne reacts with hydrogen in presence of palladium deposited on calcium carbonate as a catalyst. This leads to formation of cis-but-2-ene.
In the reaction, palladium deposited on calcium carbonate is used as a catalyst. This is known as Lindar’s catalyst. Lindar’s catalyst reduces alkynes and produces cis-alkene.
The reaction is as follows:
Thus, the reaction sequence is as follows:
 CH3−C≡CHNa/liq.NH3One equib.CH3−C≡C+CH3−ICH3−C≡C−CH3H2/Pd−CaCO3CH3−(H)C=C(H)−CH3
CH3−C≡CHNa/liq.NH3One equib.CH3−C≡C+CH3−ICH3−C≡C−CH3H2/Pd−CaCO3CH3−(H)C=C(H)−CH3
Thus, compound ‘C’ is cis-but-2-ene.
Therefore, option (B) is correct.
Note: In the reaction, palladium deposited on calcium carbonate is used as a catalyst. This is known as Lindar’s catalyst. Lindar’s catalyst reduces alkynes and produces cis-alkene. Lindar’s catalysts are heterogeneous catalyst in which palladium is deposited on calcium carbonate or barium sulphate.
