Question
Question: What structural feature distinguishes proline from other natural \(\alpha - \) amino acids? A. It ...
What structural feature distinguishes proline from other natural α− amino acids?
A. It is optically inactive.
B. It contains aromatic groups.
C. It is a dicarboxylic acid.
D. It has a secondary amine.
Solution
A bi-functional organic molecule that contains both a carboxyl group, −COOH as well as an amine group, −NH2. Amino acids derived from proteins have the amino group on the α− carbon, i.e. the carbon next to the carboxyl group.
Complete step by step solution:
Amino acids are considered to be the building blocks of proteins. The general structural formula of amino acid is given below:
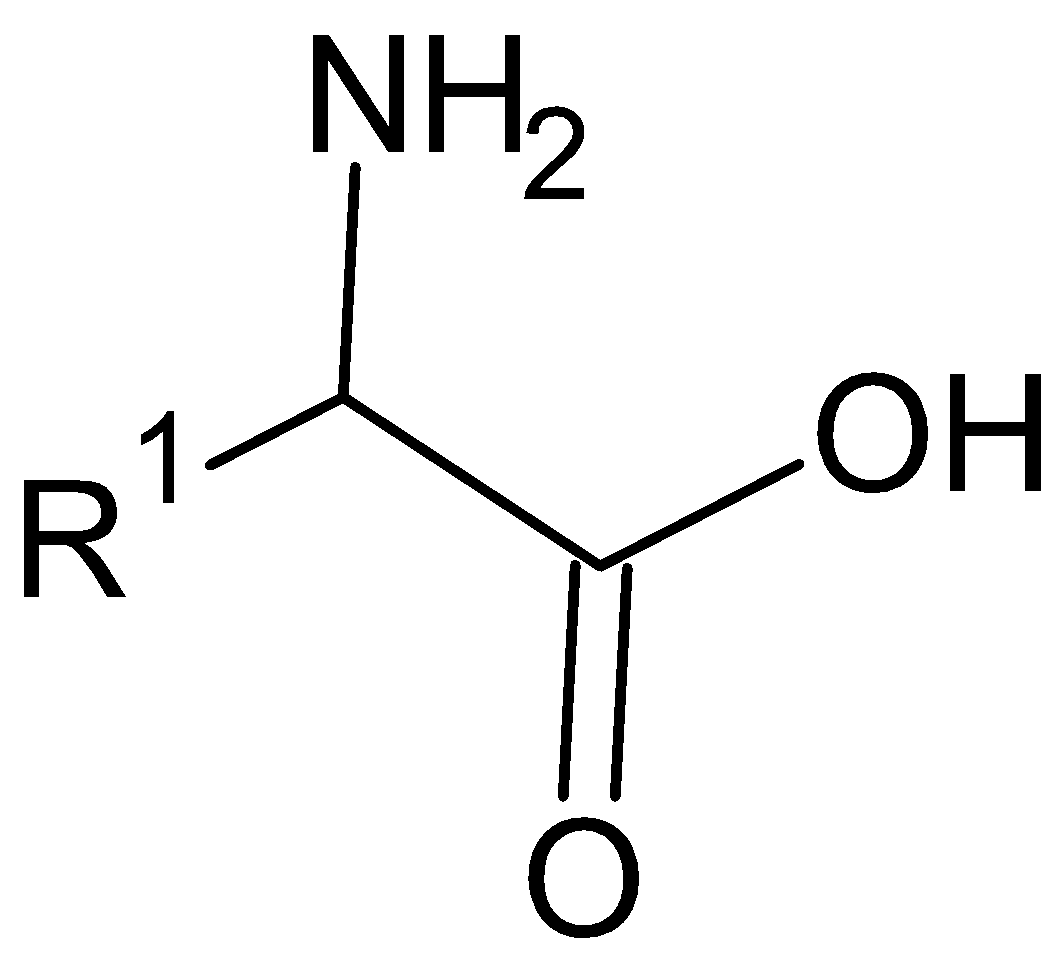
Amino acids are the structural units that make up the proteins. They join together to form short polymer chains called peptides or longer chains called either polypeptides or proteins. These polymers are linear and unbranched, with each amino acid within the chain attached to two neighboring amino acids.
Amino acids are classified as non-polar, polar amino acids with no charge, with positive charge and negative charge. Non-polar amino acids have the same number of amino and carboxyl groups, thus are neutral. They are hydrophobic and have no charge. Some examples are alanine, valine, leucine, isoleucine, phenylalanine, glycine, tryptophan, methionine and proline.
The structure of proline molecule is given below:
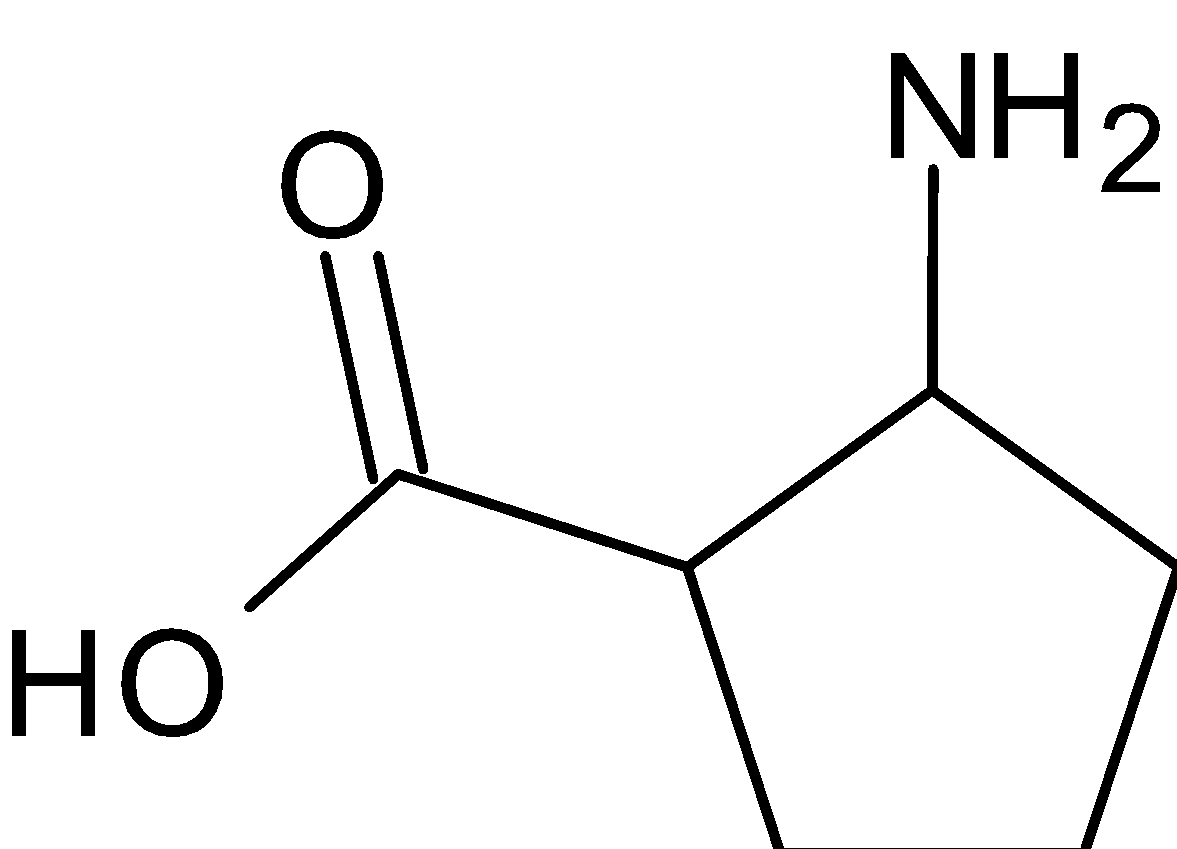
In this molecule, the same carbon is attached to the amino group and carboxyl group.
Hence proline is different from α− amino acids with a secondary amine.
So the correct option is D.
Note: There are 300 amino acids that occur in nature. The amino acids differ in the nature of the R - group attached to the α− carbon atom. The nature of the R - group determines the properties of proteins. There are compounds which are similar to proline.
