Question
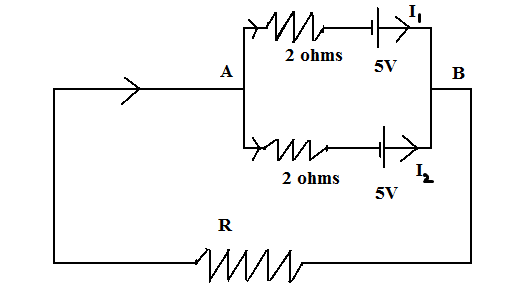
Question: What should be the voltage across the resistance R? 
Solution
To solve this question we have to first find the Kirchhoff’s rules of current which states current entering is equal to current leaving. After that, we can use the concept of emf and use the internal resistance of the cell to find the potential drop in the path. With this, we can easily find the voltage across the resistance R.
Formulae used:
I=I1+I2
Where I is the total current which is entering, I1 is the current across 1st path and I2 is the current across 2nd path.
I=rE−V
Where I is current, E is the Electromotive force (EMF) of the cell, V is the potential drop and r is the internal resistance of the cell.
Complete step by step answer:
According to Kirchhoff’s law of current, the current entering at point A should be equal to the current leaving at B. So,
⇒I=I1+I2
Here I1 is the current in the path AB upper
And I2 is the current in the path AB lower
And I is the current entering through point A
We know that
I=rE−V
So I1=r1E1−V
Where I1 is the current in the upper AB path, E1 is the Electromotive force (EMF) of the cell, V is the potential drop and r1 is the internal resistance of the cell.
⇒I1=25−V
Similarly
I2=r2E2−V
Where I2 is the current in the upper AB path, E2 is the Electromotive force (EMF) of the cell, V is the potential drop and r2 is the internal resistance of the cell.
⇒I2=25−V
From Kirchhoff’s law of current ,
I=25−V+25−V
⇒I=5−V
⇒V=5−I
So the required answer is 5−I volts.
Additional information:
Kirchhoff’s law for current conservation and energy conservation is used very commonly to solve questions related to electrical circuits. It can make the calculation of current and voltage in complex cells easy but it works under the assumption that there is no fluctuating magnetic field in the closed-loop. Electric fields and emf could be induced which causes Kirchhoff’s loop rule to break in presence of a variable magnetic field.
Note: Always remember to take care of the direction of current flow. Also, the value of the emf of the cell is important. We should always carefully see if the positive sides i.e., anode, and negative side i.e., cathode are in the same direction or not.
