Question
Question: What product would you obtain from acidic and basic hydrolysis of the N,N-diethylbenzamide?...
What product would you obtain from acidic and basic hydrolysis of the N,N-diethylbenzamide?
Solution
Amides can be hydrolyzed in either acidic or basic solution, the mechanisms are much like those of ester hydrolysis, but the reactions are much slower. Hydrolysis under acidic conditions requires strong acids.
Complete answer:
Acidic hydrolysis:
After acidic hydrolysis, N,N-diethylbenzamide gives the desired products, after the addition of water, benzoic acid is formed.
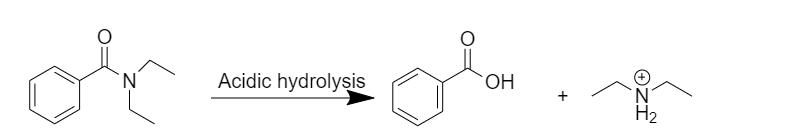
Hydrolysis under acidic conditions requires acid like hydrochloric acid, and temperature of about for several hours. The mechanism involves protonation of the amide on oxygen followed by an attack of water on the carbonyl carbon. The tetrahedral intermediate formed dissociates ultimately to the benzoic acid and protonated diethylamine.
Basic hydrolysis:
After basic hydrolysis, N,N-diethylbenzamide gives the desired products. Here, a benzoate ion is formed during the reaction.
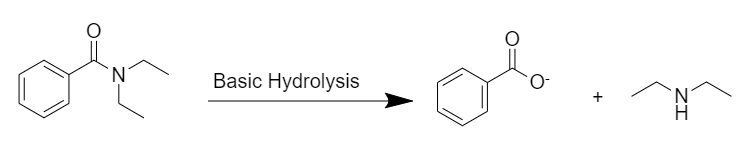
In basic hydrolysis the amide is heated with boiling aqueous sodium or potassium hydroxide. The nucleophile hydroxide ion adds to the carbonyl carbon to form a tetrahedral intermediate, which with the help of the aqueous solvent, expels the salt of benzoic acid and diethylamine.
Note:
Amides are not readily oxidized or reduced, although hydrogenation (addition of hydrogen at high temperature) in the presence of a catalyst will convert most amides into carboxylic acid to amines. The powerful reducing agent lithium aluminum hydride transforms amides into amines.
