Question
Question: What molecules prevent cell membranes from dissolving?...
What molecules prevent cell membranes from dissolving?
Solution
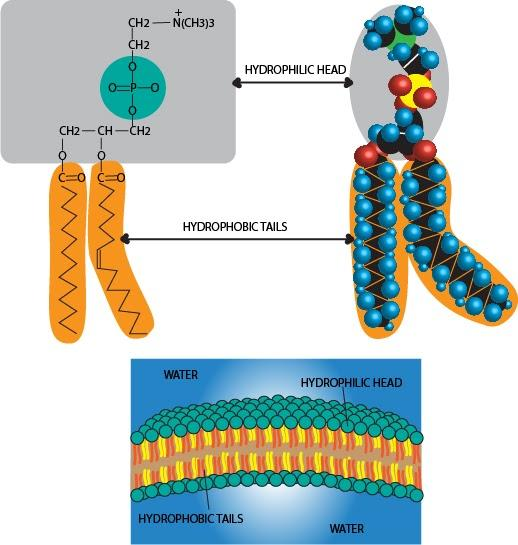
Phospholipids, also known as phosphatides, are a class of lipids. It's molecule has a hydrophilic "head" containing a phosphate group and two hydrophobic "tails" which are derived from fatty acids and joined together by a glycerol molecule. Phospholipid bilayers are critical constituents of cell membranes.
Complete answer:
The molecules which prevent the cell membrane from dissolving are lipid molecules, most importantly phospholipids. Phospholipids control and regulate the passage of ions to and fro through the cell membrane. The head of this molecule is hydrophilic while the tail is hydrophobic. The hydrophilic head dissolves readily in water while the hydrophobic head remains insoluble.
In water, phospholipids will spontaneously form a double layer called a lipid bilayer. In this bilayer, the hydrophobic tails of the phospholipid molecules are sandwiched between two layers of hydrophilic heads. In this way, only the heads of the molecules are exposed to the water, while the hydrophobic tails interact only with each other. This phospholipid bilayer allows the passage of certain substances which is achieved by embedding several protein molecules in and through the lipid layer. Many of these membrane proteins also contain attached carbohydrates on the outside of the phospholipid bilayer, allowing it to form hydrogen bonds with water. Thus, preventing the dissolution of the cell membrane.
Note:
The synthesis of phospholipids occurs in the cytosolic side of the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) membrane. In due course, a vesicle will bud off from the ER with phospholipids destined for the cytoplasmic cellular membrane on the vesicle's exterior leaflet and phospholipids destined for the exoplasmic cellular membrane on its inner leaflet.