Question
Question: What Kossel-Lewis approach of formation of chemical bonds follow? A. Avogadro’s law B. Octet rul...
What Kossel-Lewis approach of formation of chemical bonds follow?
A. Avogadro’s law
B. Octet rule
C. Kinetic theory of gases
D. VSEPR Theory
Solution
As we know that Kossel-Lewis developed a theory of chemical bonding to explain formation of chemical bonds according to which each atom tries to attain octet configuration in its valence shell.
Complete answer:
- Kossel-Lewis approach of formation of chemical bond follows Octet rule, according to which each atom tries to attain octet configuration in its valence shell by gaining or losing or by sharing of electrons.
- Let’s discuss about Lewis approach towards chemical bonding:
Lewis introduced the concept of representing valence electrons with dots that are called Lewis symbols. It is found that these symbols provide the valence electrons or we can say the number of outermost electrons of the atom, that can help to determine the valency of the atom. We can see the Lewis symbol for Oxygen atom:
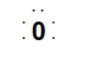
- Now let’s discuss about Kossel approach towards chemical bonding:
As we know that alkali metals are highly electropositive elements and halogens are highly electronegative elements in the periodic table. It is found that Alkali metals, in the process of attaining stability, tend to lose electrons and will get positive charge. And halogens, in the process of gaining stability, tend to gain electrons and will get negative charge.
- And as we have seen during these processes the alkali metals as well as halogens will acquire octet configuration and also duplet configuration.
- Hence, we can conclude that the correct option is (b) that is Kossel-Lewis approach of formation of chemical bonds following Octet rule.
Note: - Kossel-Lewis approach of bonding differs from the modern views. As according to Kossel-Lewis, bond is formed by mutual sharing or by transfer of electrons in between two atoms.
- Whereas, according to modern views, a chemical bond is formed when there is a net decrease in energy due to attractive and repulsive forces in between two atoms.
