Question
Question: What is Z in the above sequence of reactions? \( {C_2}{H_5}Cl\xrightarrow{{KCN}}X\xrightarrow{{{H...
What is Z in the above sequence of reactions?
C2H5ClKCNXH2/catalystYCHCl3,alc.kOHZ
Solution
Alkyl halides are the compounds consisting of alkyl parts attached with the halogen atom. The alkyl cyanides upon treatment with potassium cyanide gives alkyl cyanide. The alkyl cyanides upon hydrogenation forms amines. Amines treated with chloroform and potassium hydroxide form isocyanides.
Complete answer:
Given compound is ethyl chloride with the molecular formula of C2H5Cl . In this the ethyl group is attached with the chlorine atom. The ethyl cyanide upon treatment with potassium cyanide, the chlorine atom in ethyl cyanide was replaced by cyanide group which is a nucleophilic substitution reaction.
Thus, ethyl cyanide was formed with the molecular formula of C2H5CN . When ethyl cyanide is treated with chloroform and alcoholic potassium hydroxide the unpleasant or pungent smell compounds isocyanates will be formed.
The formation of isocyanate from primary amines is an important reaction called as carbylamine reaction. The fumes of isocyanates are dangerous and should not be inhaled.
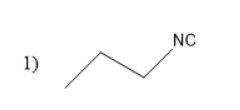
Thus, ethyl cyanide forms propyl amine with the molecular formula of C3H7NH2 . This propyl amine undergoes carbylamine reaction to form propyl isocyanates.
The structure of propyl isocyanate is
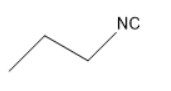
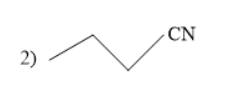
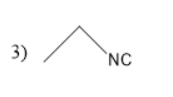
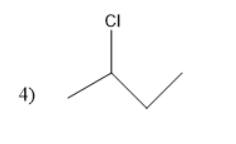
Thus, in the given question the answer matches with the option 1 .
Thus, option 1 is the correct one.
Note:
The primary amines only undergo the carbylamine reaction. Propyl amine is the primary amine as the amine group is attached to the only one carbon atom and thus propyl amine undergoes carbylamine reaction. Precautions must be taken while using cyanide compounds in the laboratory.
