Question
Question: What is Williamson’s ether synthesis? Give an equation....
What is Williamson’s ether synthesis? Give an equation.
Solution
In this reaction, an ether is formed from an organohalide. The mechanism used in this reaction is SN2 mechanism.
Complete answer:
The Williamson ether synthesis is an organic reaction, forming an ether from an organohalide and a deprotonated alcohol. This method is suitable for the preparation of a wide variety of unsymmetrical ethers. The reaction was discovered by Alexander William in 1850. It involves the attack of alkoxide ion on a primary halide via SN2 mechanism. This reaction is very important in the history of organic chemistry because it helped to prove the structure of ethers. However, If the halides are sterically demanding and there are accessible protons in the β-position, the alkoxide will act as a base, and side products derived from elimination are isolated instead.
The mechanism for Williamson synthesis is:
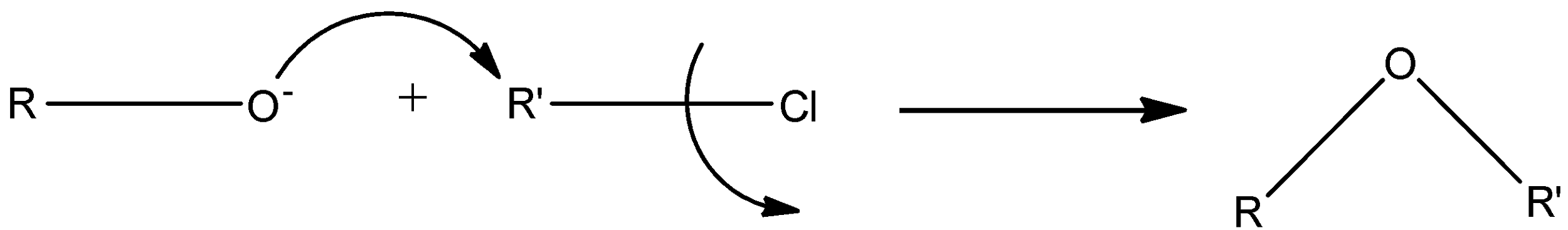
An example of Williamson ether synthesis is:
{C_2}{H_5}{O^ - }N{a^ + } + {C_2}{H_5}Cl \to {C_2}{H_5}O{C_2}{H_5} + N{a^ + }C{l^\\_}
The Williamson ether synthesis is an SN2 bimolecular nucleophilic substitution reaction. In an SN2 reaction, the nucleophile attacks the anti-bonding orbital of the electrophile. It occurs in a concerted mechanism (all at once). The rate of reaction of an SN2 reaction depends mainly on the leaving tendency of the leaving group. The leaving group must be sufficiently electronegative, like a halide. In Williamson ether synthesis, alkoxide ion (RO−) acts as the nucleophile which attacks the electrophilic carbon with the leaving group.
Note:
Remember that the reaction follows SN2 mechanism. SN2 mechanism is a concerted mechanism, therefore finally an inverted product is formed.
