Question
Question: What is the type of hybridization in Ethane \[\left( {{C_2}{H_6}} \right)\]\[?\]...
What is the type of hybridization in Ethane \left( {{C_2}{H_6}} \right)$$$$?
Solution
First we know hybridization is the concept of mixing atomic orbitals into new hybrid orbitals suitable for the pairing of electrons to form chemical bonds in valence bond theory. Then we know the types of hybridization. Then mention the type of hybridization in ethane with explanation.
Complete answer:
Consider the Lewis structure for Ethane (C2H6)
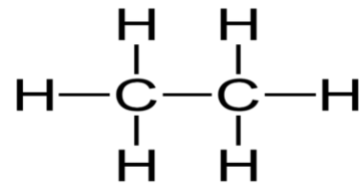
Here we can count 4 sigma bonds and 0 lone electron pairs (unshared electrons) around the central atom (carbon). Sigma bonds are overlaps of electron clouds between two atoms nuclei (a single bond). Pi bonds are bonds that do not get hybridized and are double and triple bonds. However, there is always 1 sigma bond in each double and triple bond.
The hybridization of sigma bonds and lone electron pairs goes as such:
1 cloud: sp
2 clouds: sp2
3 clouds: sp3
4 clouds: sp3d
5 clouds (maximum): sp3d2
The four electron groups surrounding each carbon. It made four identical bonds in a perfect tetrahedral geometry, which means it needed four identical orbitals to make those bonds.
Each carbon has to hybridize one 2s and three 2p orbitals in order to generate four identical sp3orbitals that are compatible in symmetry with hydrogen's 1s orbitals.
Therefore, each C−H bond in (C2H6)is between an sp3 of carbon and a 1s of hydrogen, i.e. an s{p^3}$$$$ - s connection, and each C−C bond is an sp3-sp3 connection.
Hence, the type of hybridization of Ethane (C2H6)is sp3 hybridization.
Note:
Note that hybridization is also known as orbital hybridisation. Sigma bond is a chemical bond formed by the linear or co-axial overlapping of the atomic orbitals of two atoms. A pi bond is a type of covalent bond that exists between atoms where the electrons are on top and bottom of the axis connecting the nuclei of the joined atoms.
