Question
Question: What is the titration curve of glycine?...
What is the titration curve of glycine?
Solution
Hint : We know that equivalence point is a point in titration at which the amount of titrant added can completely neutralize the analytic solution. At this equivalence point in an acid-base titration, the number of moles of base becomes equal to the number of moles of acid and then the solution is only left with salt and water.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
The process of titration is a chemical analysis which is used to find out the concentration of unknown solution by adding a solution of known concentration. The known solution is known as titrant and the unknown solution is known as analytic. Equivalent point is the point where the concentration of the acid and base is equivalent. Strong acids and bases neutralize each other completely at equivalence points.
Below is a typical curve for the titration of glycine with NaOH.
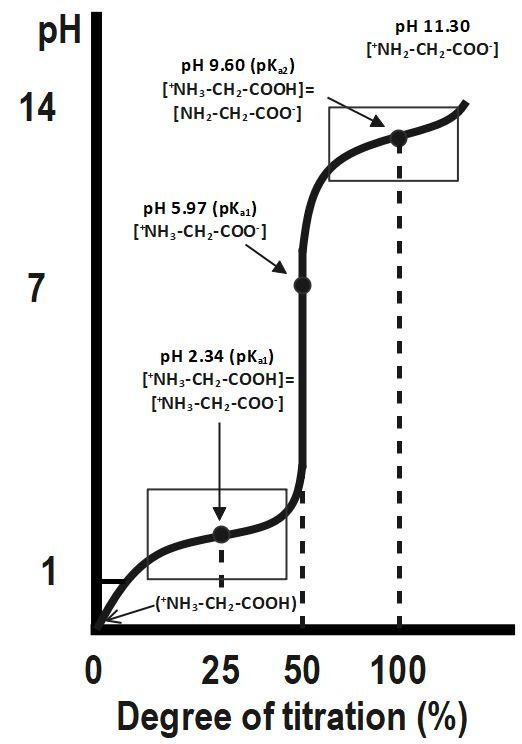
Although we often write glycine as NHCOOH, it is really a zwitterion, N+H3CH2COO−. The fully protonated form of glycine is N+H3CH2COOH. The protonated form of glycine ionizes in two steps:
The loss of H+ from the carboxyl group; +NH3CH2COOH+H2O⇌+NH3CH2COO−+H3O+
The loss of H+ from the less acidic NH3+ group +NH3CH2COO−+H2O⇌NH2CH2COO−+H3O+
The first equivalence point, at 50 titration, is at pH=5.97.
Halfway between 0 and 50 % titration (i.e. at 25 ) pH=pKa1. The second equivalence point, at 100 titration, is at pH=11.30. Halfway between 50 and 100 (i.e. at 75 ), pH=pKa2.
At 50 titration, the glycine exists as a zwitterion. This is the isoelectric point pI. At this point, pH=pI .
pI=21(pKa1+pKa2) For glycine, pKa1=2.34, pKa2=9.60, and pI=5.97.
Each amino acid has a characteristic set of pK and pI values. Thus, you can use a titration curve to identify an unknown amino acid.
Note :
Remember that pH value in chemistry is a method of measurement of the acidic or the basic nature of a solution or substance. A substance or solution is acidic if it has high concentration of hydrogen ions and is basic if it has high concentration of hydroxide ions or the low concentration of hydrogen ions. pH has an important role in reflecting the chemical properties of the solutions. pH have various activities such as control of the microbial or the biological functions, properties of certain chemicals and their behaviour.
