Question
Question: What is the test to differentiate between pentan-2-one and pentan-3-one. A.Iodoform test B.Bene...
What is the test to differentiate between pentan-2-one and pentan-3-one.
A.Iodoform test
B.Benedict’s test
C.Fehling’s test
D.Aldol condensation
Solution
To answer this question, you should recall the test to differentiate between carbonyl compounds at second position and at other intermediate positions. This test involves the reaction of iodine, a base and a methyl ketone gives a yellow precipitate.
Complete step by step answer:
When Iodine and sodium hydroxide are added to a chemical species containing either a methyl ketone or secondary alcohol with a methyl group in the alpha position, a pale yellow precipitate i.e. iodoform or triiodomethane is formed.
The general haloform reaction of methyl ketones can be represented as:
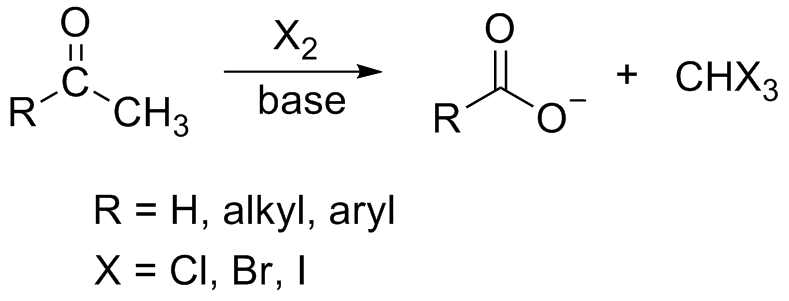
In the reaction, in the first step, the hydroxide ion removes the acidic alpha hydrogen from the ketone resulting in the formation of an enolate ion. This newly formed enolate anion further displaces an iodide ion from the iodine molecule. This process repeats and ultimately the hydroxide ion forms a bond with the carbonyl carbon.
The final result is the reformation of the carbonyl group and the elimination of the X3− anion. Only methyl ketone group gives positive iodoform so the compound pentan-2-one will give iodoform test and pentan-3-one will not give a positive iodoform test.
Hence, the correct answer to this question is option A.
Note:
If an aldehyde gives a positive iodoform test, then it must be acetaldehyde since it is the only aldehyde with a CH3C=O group. The mechanism is that:
First, the Hydroxide ion removes acidic alpha hydrogen. This results in the formation of an enolate ion. The enolate anion then goes on to displace an iodide ion from the iodine molecule. This process repeats twice to give R−CO−CI3.
Now, a hydroxide ion forms a bond with the carbonyl carbon. This leads to the reformation of the carbonyl group and the elimination of the CI3− anion. A R−COOH group is also formed. The carboxylic acid group and the basic CI3− ion neutralize each other. Thus, iodoform is precipitated.
