Question
Question: What is the term for mature sperm cells?...
What is the term for mature sperm cells?
Solution
Sperms are flagellated cells with a whip-like tail except nematode worms, decapods, diplopods. In case of higher vertebrates these cells are produced and matured in testes which are the reproductive organs in male.
Complete answer:
Sperm refers to the male reproductive cells which are produced by most animals. In case of higher vertebrates these cells are produced and matured in testes which are the reproductive organs in male. They are flagellated cells with a whip-like tail except nematode worms, decapods, diplopods.
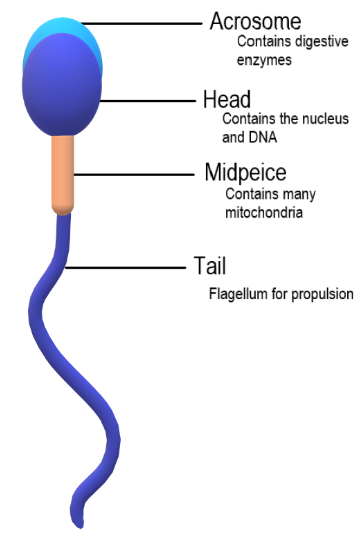
The sperms are the male sex cells which fuses with the female sex cell known as ova to form zygote. This formed zygote then develops into a new organism. The mature sperm cells are distinguished into two parts: head and tail. The head varies from species to species in shape. In humans, the shape of the head of sperm is almond shaped and flattened.
Head portion of the cell contains the nucleus and the chromosome which is the genetic material which is responsible for the transmitting characteristics to the individual. These characteristics include color of eyes, hairs and skin.
Normally in every human being there are 46 chromosomes (23 pairs) which are responsible for the genetic identity of humans. The sperm cells have 23 chromosomes and ova cells have 23 chromosomes. They are haploid in nature, i.e., they consist of only one set of chromosomes. These two haploid cells combine and form a diploid cell known as zygote. Zygote has 46 chromosomes (diploid).
Each mature sperm cell is named as spermatozoa , which is haploid in nature produced by meiosis. Mature sperm cells consist of the head, neck, middle piece and tail. 55 to 65 micrometers is the average length of each spermatozoa.
Note:
Sperm refers to the male reproductive cells which are produced by most animals. Head portion of the cell contains the nucleus and the chromosome which is the genetic material which is responsible for the transmitting characteristics to the individual. Normally in every human being there are 46 chromosomes (23 pairs) which are responsible for the genetic identity of humans.
