Question
Question: What is the structure of \(XeO{F_4}\)? (A) Square pyramidal (B) Trigonal bipyramidal (C) Pyram...
What is the structure of XeOF4?
(A) Square pyramidal
(B) Trigonal bipyramidal
(C) Pyramidal
(D) Square bipyramidal
Solution
First identify the central atom and check for the number of electrons that form bonds and the lone pairs left behind. Now draw the lewis structure of the molecule considering the repulsions between the lone pairs and the bond pairs and identify the shape of the molecule.
Complete step by step answer:
-We will first try and draw the Lewis structure of the compound XeOF4.
Here we know that an atom of fluorine can bind with only one atom while an oxygen atom can bind with only 2 atoms and the compound contains 6 atoms in total. So, the central atom will be xenon (Xe).
We all know that Xe is a noble gas and hence it will contain 8 electrons in its valence shell, oxygen has 6 electrons and fluorine has 7 electrons. The 4 F atoms will form a single bond each with the Xe atom and the oxygen atom will form a double bond with Xe atom. So, its structure will be as follows:
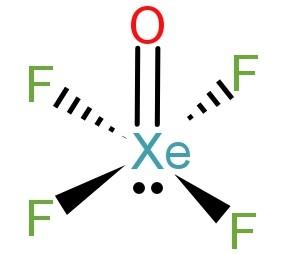
As we talked above Xe has 8 electrons in its valence shell, out of which 4 electrons form single bonds with 4 F atoms and 2 electrons form a double bond with 1 O atom. The Xe atom is left with a lone pair of electrons.
-Now due to lone pair – bond pair repulsion the Xe-F bonds will remain away from the lone pair. The Xe-O and the Xe-F bonds also undergo bond pair – bond pair repulsion due to the lone pairs of F and O atoms. Due to all this all the 4 Xe-F bonds will lie in one plain to minimise the repulsion within the compound. Hence the structure of XeOF4 will be square pyramidal and the hybridisation of the molecule is sp3d2.
So, the correct option will be: (A) Square pyramidal
Note: While determining the structure of compounds, always check for the valance electrons of the central atom and do not forget to consider the lone pair of atoms. Also the order of repulsion of bond pairs (bp) and lone pairs (lp) is: lp - lp > lp - bp > bp – bp
