Question
Question: What is the structure of glycine at pH 5?...
What is the structure of glycine at pH 5?
Solution
In the statistical mean, the isoelectric point is the pH at which a molecule has no net electrical charge or is electrically neutral. pH is the conventional abbreviation for the isoelectric point (I). pI, on the other hand, is also utilised. This article employs the abbreviation pI for the sake of brevity. The pH of the surrounding environment affects the net charge on the molecule, which might become more positively or negatively charged due to the addition or loss of protons (H+).
Complete answer:
The amino acid glycine has a single hydrogen atom in its side chain. It has the chemical formula NH2CH2COOH and is the simplest stable amino acid (carbamic acid is unstable). One of the proteinogenic amino acids is glycine. It is encoded by all codons that begin with the letter GG (GGU, GGC, GGA, GGG). Because of its compact nature, glycine is essential for the development of alpha-helices in secondary protein structure. It is also the most prevalent amino acid in collagen triple-helices for the same reason. Glycine is also an inhibitory neurotransmitter, and blocking its release in the spinal cord can result in spastic paralysis from uncontrolled muscular contraction.
It is primarily notable for its acid–base characteristics. Glycine is amphoteric in aqueous solution: at low pH, it may be protonated with a pKa of approximately 2.4, while at high pH, it loses a proton with a pKa of about 9.6. (precise values of pKa depend on temperature and ionic strength).
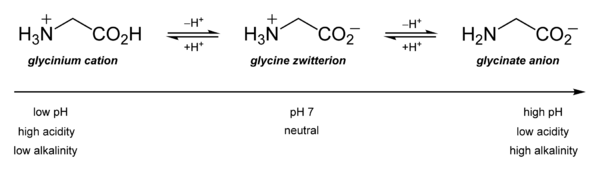
pI=2pKa1+pKa2=22.34+9.60=211.94=5.97
Glycine has a net positive charge below pH 5.97, but it has a net negative charge above pH 5.97.
Hence it is isoelectronic at pH 5.
Note:
Although glycine can be extracted from hydrolyzed protein, it is not employed in industrial manufacturing since chemical synthesis is more convenient. The amination of chloroacetic acid with ammonia, which produces glycine and ammonium chloride, and the Strecker amino acid synthesis, which is used in the United States and Japan, are the two primary methods. This method produces around 15 thousand tonnes per year.
