Question
Question: What is the role of sclera, aqueous humor and retina in the eye?...
What is the role of sclera, aqueous humor and retina in the eye?
Solution
Eyes are very sensible as well as very necessary sensory organs that provide vision to all the organisms. The parts of the eye are retina, lens, cornea, eyeball, ciliary muscle etc. A fluid is present in the eye, known as aqueous humor, which is required for maintaining the health of the eyes.
Complete answer:
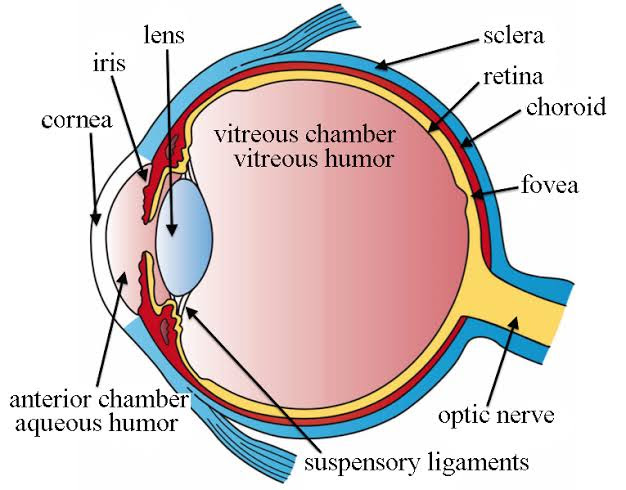
1. Sclera – It is the tough outermost protective layer of the connective tissue of the eye which is joining the cornea. It is the visible white part of the eye. The sclera has a transparent covering, called the conjunctiva which helps lubricate the eye and protect it from microbes. The sclera helps in maintaining the shape of the eyeball, which is about one inch (25mm) in diameter. Besides that, it is providing attachment to muscles that move the eyes.
2. Aqueous Humor – it is a transparent fluid present in the eye, especially within the anterior and posterior chamber. This liquor is produced by the ciliary body in the eyes. At the back of the retina, it acts as the film of the camera. It is constantly produced into the posterior chamber and then flows through the pupil into the anterior chamber. It is located between the lens and retina. It acts as the reflective medium but functions as the refractive medium. It regulates the intraocular pressure in the eyes as well as maintains the eyeball by regulating its shape and size. It protects the eyes by blocking the dust, bacteria etc as well as helps in the protection of the eyes. It provides nutrients and oxygen for ocular tissue including the posterior cornea, trabecular meshwork, and lens. It also helps in removal of metabolic by-products from intraocular cells.
3. Retina – It is the innermost layer of blood vessels and nerves that serves as the “film” of the eye. These are sensory tissues which lining the back two-thirds of the eyeball. The retina receives visual images and transmits signals to the optic nerve through its nerve endings, the rods and cones. The retina consists of two layers: the sensory retina, which contains nerve cells that possess visual information and send it to the brain; and the retinal pigment epithelium (RPE), which lies between the sensory retina and the wall of the eye. It comprises millions of photoreceptors converting light rays into electrical impulses which are then relayed to the brain through the optic nerve.
Note:
The main function of ‘aqueous humor’ is to provide nutrition like vitamin C to the lens by draining the metabolism. It has a high amount of lactic acid and the pyruvic acid in it and also possesses salt, sugar, collagen and water. Improper drainage of the aqueous humor can cause an increase in intraocular pressure (pressure inside the eye). This increase can result in loss of vision or contribute to the development of glaucoma. Issues with aqueous humor drainage can be treated surgically.
