Question
Question: What is the retention of configuration?...
What is the retention of configuration?
Solution
Retention and inversion are opposite to each other due to their different properties. Retention of configuration can be seen in SN1 whereas inverse of the configuration can be seen in SN2 reaction.
Complete Solution :
- In the given question we have to explain the term retention of configuration.
- So, firstly we should know what absolute configuration and relative configuration are. In the absolute configuration, the atom does not depend on another atom or molecule.
- Whereas in relative configuration the position of an atom depends or is told concerning the position of another atom or molecule.
- So, in the retention of configuration, both the absolute and relative configuration do not change their structure and the position of the atom after the completion of the reaction.
- Or we can say that the R position remains R and S position remains S after the reaction, they do not convert into each other.
- In R configuration if the priority groups are present in the clockwise direction then are assigned as R configuration whereas if the priority groups are present in the clockwise direction then are assigned as S configuration.
- For example, the SN1 reactions occur through the retention of configuration.
An example is when 2-iodo - 2 phenyl butane i.e. S configuration is hydrolysed by SN1 reaction through the retention of the configuration then they form one S and one R configuration.
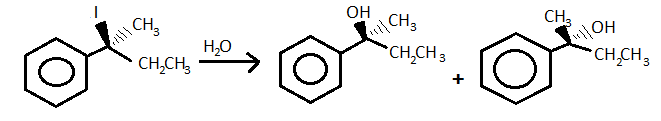
Note: Inverse of the configuration is opposite to retention because in inverse either the absolute or relative atom or molecule changes its position from R to S or from S to R configuration. Also, the inverse of the configuration can be seen in SN2 reaction.
