Question
Question: What is the propane gas chemical formula?...
What is the propane gas chemical formula?
Solution
We can say that the chemical formula of a compound is a symbolic portrayal of its chemical composition. Chemical formulas give knowledge into the elements that comprise the particles/molecules of a compound and furthermore the proportion wherein the atoms of these components consolidate to give such molecules.
Complete answer:
We have to know that the chemical formula ' normally' alludes to the molecular formula of a compound. We can describe the compositions of chemical compounds in many ways. They are,
Molecular formula
Empirical formula
Structural formula
The molecular formula gives understanding into the quantity of components present in a compound. In molecular formulas, the components are signified by their particular symbols and the quantity of particles of every element in the particle is represented as subscript.
The empirical formula of a chemical formula addresses the proportion of the components present in that compound. Empirical formulae are typically acquired dependent on the examination of experimental information.
The structural formula of a substance compound gives understanding into the arrangements of the atoms present in the compound.
We know that propane is an alkane. Generally, alkanes have a chemical formula of CnH2n+2. In propane, there are three carbon atoms present, so the value of n will be three.
Let us now substitute the value of n in the general formula of alkanes. So, C3H2(3)+2 becomes C3H8. The chemical formula of propane is C3H8. The molecular formula of propane is also C3H8.
We can give the structural formula of propane as,
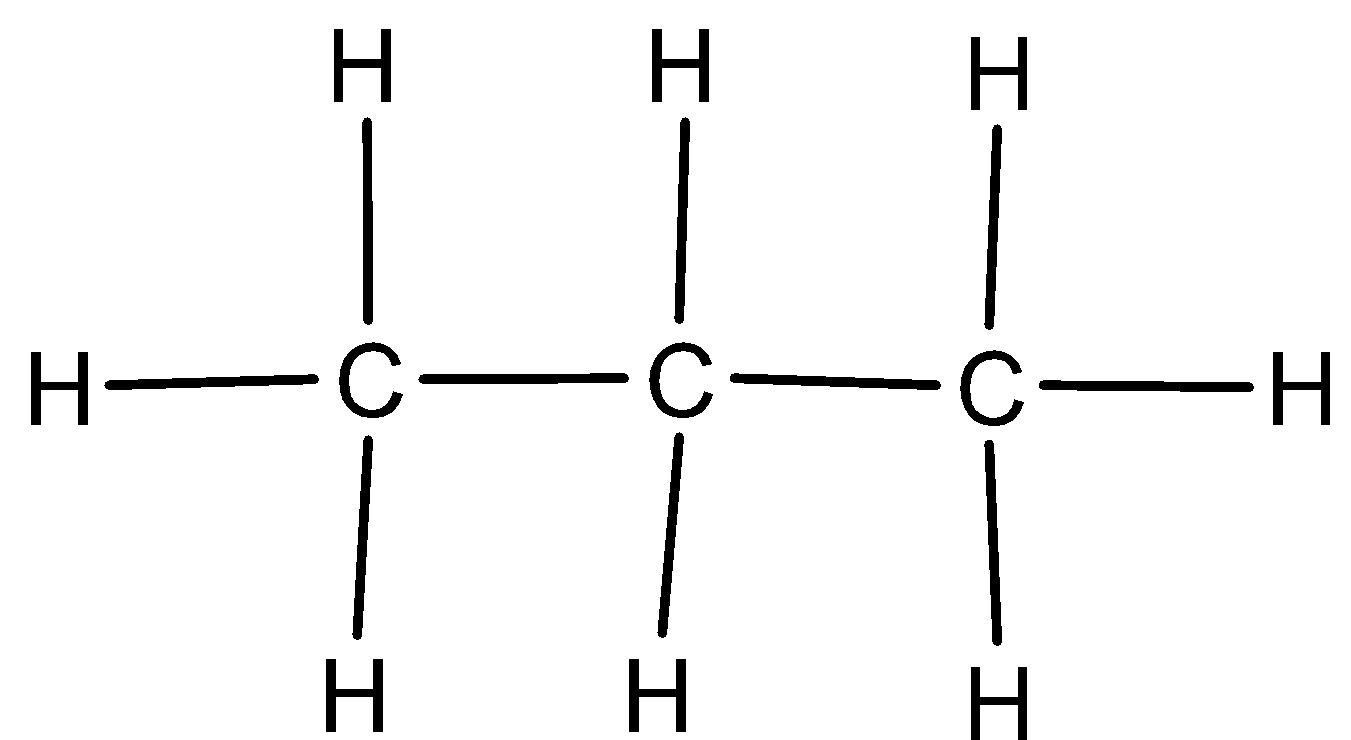
Note:
We can write the expanded chemical formula of propane as CH3CH2CH2. One mole of propane has three atoms of carbons, and eight atoms of hydrogen. It is a colorless and odorless gas which is used in buses as biofuel, as major gas in blowtorches, and in hot air balloons.
