Question
Question: what is the product of the following reaction? \( C{H_3}CHO\xrightarrow[\vartriangle ]{{Se{O_2}}} ...
what is the product of the following reaction?
CH3CHOSeO2△
Solution
Selenium dioxide is an oxidizing agent. Selenium dioxide oxidizes allylic positions of alkenes to either alcohols or carbonyl groups. It also oxidizes alpha methylene group on a carbonyl compound to give 1, 2 dicarbonyl compounds. Selenium dioxide is an acidic oxide and dissolves in water to form selenous acid with molecular formula H2SeO3 . Moreover, selenium dioxide exists as a one dimensional polymeric chain with alternating selenium and oxygen atoms.
Complete answer:
The Riley oxidation is a type of selenium dioxide mediated oxidation of alpha methylene groups adjacent to carbonyls. The reaction of acetaldehyde with selenium dioxide involves the following steps:
Step 1: acetaldehyde undergo keto-enol tautomerism:

During the keto-enol tautomerism of acetaldehyde deprotonation of alpha carbon atoms takes place leading to the formation of enolate ions, this is followed by protonation of the enolate ion to form an enol.
Step 2: Selenium dioxide attacks the enol form:
Selenium dioxide attacks the enol from the product as shown.

Step 3: Oxidative rearrangement:
The above product undergoes oxidative rearrangement.
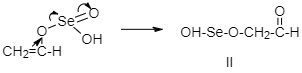
Step 4: Removal of water and selenium:
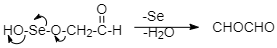
There is a removal of selenium and water from the above product to form the final product which is glyoxal.
Note:
The smallest aldehyde with the chemical formula OCHCHO is glyoxal. Glyoxal is a crystalline solid which appears to be white at low temperature and yellow near the melting point. In liquid state it appears yellow while in vapour form it is green in color. At commercial or large scale it can be prepared either by gas phase oxidation of ethylene glycol in the presence of a catalyst such as copper or silver or by liquid phase oxidation of acetaldehyde with nitric acid.
