Question
Question: What is the primary acceptor of \[CO2\] in \(C4\) plants? What is the first compound formed as a res...
What is the primary acceptor of CO2 in C4 plants? What is the first compound formed as a result of primary carboxylation in the C4 pathway?
Solution
C4 plants follow a pathway known as C4 pathway which helps them to fix carbon dioxide even when the concentration of oxygen is more than carbon dioxide.
CO2 receptor fixes it in the presence of an enzyme known as “PEP Carboxylase”. Pep carboxylase converts the three-carbon compound into a four-carbon compound after reacting with carbon dioxide. This mechanism is used to prevent photorespiration in plants to conserve energy.
Complete answer:
C4 pathway or “Hatch- Slack Pathway” is a mechanism in plants to fix the atmospheric carbon dioxide to produce energy.
Although there are various types of pathways used by the plants like- C4 pathway, CAM pathway, C4 pathway is used by plants known as C4 plants.
These plants are characterized by the presence of bundle sheath cells in the leaves.
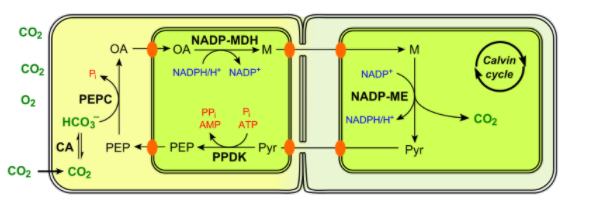
In C4 plants, the atmospheric Carbon dioxide is accepted by a molecule known as “PEP” (phosphoenolpyruvate). This is a three-carbon compound and acceptance of Carbon dioxide in the presence of PEP carboxylase by PEP results in the formation of a molecule which is a four- Carbon compound known as “Oxaloacetic acid”.
Oxaloacetic acid now converts into Malic acid, also known as malate at the expense of one NADPH.
All of these reactions take place in an organelle called “mesophyll cells”.
Now malate exits the mesophyll cell and now enters inside the organelle known as “Bundle sheath Cell”
This cell inhibits the entry of oxygen inside the cell, preventing photorespiration, a process which is not beneficial for the plant.
Malate now enters the Calvin cycle taking place inside bundle sheath cells and producing glucose molecules while the end product of the cycle i.e. pyruvate now exits the bundle sheath cells.
Pyruvate again enters mesophyll cells to convert into Phosphoenol Pyruvate at the expense of one ATP molecule.This cycle repeats in C4 plants and helps them to generate glucose.
C4 pathway takes place in those plants which are prone to fix the carbon dioxide using a process known as Photorespiration. As C4 plants get exposed to lower carbon dioxide concentration, sometimes Rubisco reacts with oxygen rather than carbon dioxide. This results in the expenditure of energy and almost zero energy molecule formation. Hence, this process is harmful because it does not fix carbon dioxide to produce energy.
So C4 plants use the C4 pathway to maintain the higher Carbon dioxide concentration around the bundle sheath cells and inhibits the entry of oxygen inside the cell.
So the answer to the question above will be- The primary acceptor of Carbon Dioxide is PEP (Phosphoenolpyruvate) and First compound formed as a result of its Oxaloacetic acid.
Note: Although C4 pathway helps the plant to conserve the nutrients and energy, it is a long and complex process. Plants might go the C4 pathway during summer (hot or dry climate) but during winters the process becomes more complex. So, the plants should choose the C3 pathway to produce energy. C4 pathway can be seen in some plants like- corn and sugarcane and some types of shrubs.
C3 plants lack in a way that they do not possess Kranz Anatomy. That is, they do not involve bundle sheath cells to fix CO2 but only mesophyll cells.
