Question
Question: What is the Phenotypic Ratio of the F\[2\] generation of monohybrid cross? A. \[1:1\] B. \[2:1\]...
What is the Phenotypic Ratio of the F2 generation of monohybrid cross?
A. 1:1
B. 2:1
C. 3:1
D. 1:4
Solution
Monohybrid cross is defined as a mating or cross between two different organisms which have different variations or alleles in only one genetic locus of interest. It is a cross between two types of plants belonging to the same species, but considering transmission of only one character. Example is a cross between a dwarf plant and a tall pea plant considering only the height of the parent trees.
Complete answer:
The below image containing the table describes the pure breed cross between tall and dwarf plants. The top alleles are from female gamete and side alleles are from male gamete. The crossing process is displayed by a table named Punnett Square, discovered by a scientist Gregor Mendel.
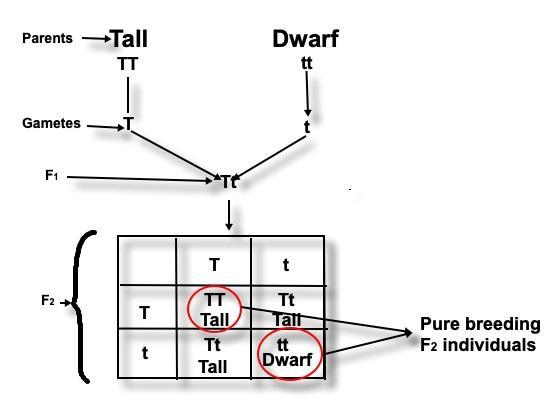
In the F1 generation, tall plants are obtained. On self-fertilizing F1 plants, F2generation plants are obtained, which are four in number. There are three tall plants and only one dwarf plant. The phenotypic ratio is 3:1and the genotypic ratio is 1:2:1 since two pure breeding individuals are obtained in the cross.
Option A 1:1: Since there are more tall plants than dwarf plants, the ratio is wrong.
Option A is not correct
Option B 2:1: Since the strength of tall plants is thrice that of dwarf plants, the ratio is wrong.
Hence, Option B is not correct
Option C 3:1: Since the count of tall plants is thrice that of dwarf plants, the given ratio is not wrong.
So, Option C is not correct
Option D 1:4: In this option, the count of dwarf plants is more. This is not probable here.
Option D is correct
Therefore, the correct answer is option D.
Note:
Phenotype of an organism is the sum of observable characteristics. Genotype of an organism is defined as the set of genes, which it carries. Phenotype is influenced by both the environment and genotype. Differences in genotypes can lead to the production of different phenotypes. Phenotype is also affected by the change in environment, producing different colors of species in different areas.
