Question
Question: What is the nitrogen content of urea? A.) \(54\% \) B.) \(40\% \) C.) \(46\% \) D.) \(56\% \...
What is the nitrogen content of urea?
A.) 54%
B.) 40%
C.) 46%
D.) 56%
Solution
Urea is widely used in the agricultural industry for the purpose of a fertilizer or urea is also used as an additive in feed of animals. Urea has the highest nitrogen content among all the nitrogenous fertilizers.
Complete step by step answer:
As we know that urea is an organic compound having the chemical formula as (H2NCONH2). The structure of urea consists of two amide groups (that is −NH2) and these amide groups are joined by a carbonyl functional group that is C=O. Urea is also known as carbamide. The structure of the urea can be represented as:
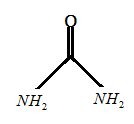
Urea is the most important nitrogenous fertilizer and it contains the highest amount of nitrogen content as compared to all other nitrogenous fertilizers. Urea contains 46% of the nitrogen in it.
Hence, option C.) is the correct answer.
Additional information:
The urea is prepared commercially by the reaction of liquid ammonia and liquid carbon dioxide. When liquid ammonia and liquid carbon dioxide react with each other at high pressure then ammonium carbamate is formed in the product and then this ammonium carbamate at very low pressure decomposes to give urea and water. This reaction can be represented as:
2NH3+CO2→NH2COONH4→H2NCONH2+H2O
The urea is widely used in the agricultural industry. Urea helps in improving the quality of the soil and is used as an organic fertilizer. Urea provides nitrogen to the plants and it also increases the yield of the crops.
Note:
As there are many advantages of urea but there are some disadvantages of urea also. When urea is manufactured then it releases harmful pollutant gases in the air. When urea exerts higher concentration of ammonia in the soil it makes the soil more acidic and thus decreases the natural fertility of the soil.
