Question
Question: What is the net force if two forces are acting in opposite directions on an object ?...
What is the net force if two forces are acting in opposite directions on an object ?
Solution
Hint : In physics, a force is any influence that, when unopposed, causes an object to change its velocity. A force can cause a mass item to change its velocity (which includes starting to move from a standstill), i.e. accelerate. Intuitively, force may be characterised as a push or a pull. A force is a vector quantity since it has both magnitude and direction. The SI unit of Newton is used to measure it (N). The letter F is used to signify force.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
Newton's laws of motion are three laws that define the connection between an object's motion and the forces acting on it in classical mechanics.
The third law says that when one item exerts a force on another, the second object exerts a force on the first object that is equal in magnitude but opposite in direction. According to the third law, all forces between two things are equal in size and opposite in direction: if one object A exerts a force FA on another item B, then B simultaneously exerts a force FB on A, and the two forces are opposite in direction:
Fnet=FA−FB
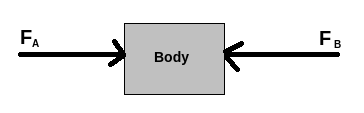
According to the third rule, all forces are interactions between distinct bodies or various regions within one body, and hence no force exists that is not accompanied by an equal and opposing force. In some cases, one of the two bodies, say Body A, determines the magnitude and direction of the forces fully; the force exerted by Body A on Body B is termed the "action," and the force exerted by Body B on Body A is called the "reaction."
The net force on an item is zero if two forces of equal magnitude but opposing diversity operate on it (null vector).
Note :
The law of conservation of momentum was derived from Newton's third law; however, conservation of momentum is the more fundamental idea (derived from Galilean invariance via Noether's theorem), and holds in cases where Newton's third law appears to fail, such as when force fields as well as particles carry momentum, and in quantum mechanics.
