Question
Question: What is the nature of the carbon atom marked with an asterisk (*) sign in the given compounds? ![]...
What is the nature of the carbon atom marked with an asterisk (*) sign in the given compounds?
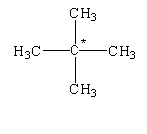
Solution
The carbon has four valence electrons that means it can bind with four other atoms to form a compound. The alkanes can be differentiated into primary, secondary, tertiary, and quaternary on the basis of the number of other carbon atoms attached to the central carbon.
Complete step by step answer:
The given structure is shown below.
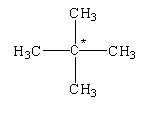
In this structure, the carbon atom is bonded to four different carbon atoms. Therefore, it is determined as a quaternary alkane.
The given compound is known as neopentane.
When the carbon atom is attached to four different groups then the central carbon atom is known as asymmetric carbon or chiral carbon.
When the compound having a chiral compound is rotated it gives a non-superimposable mirror image.
In a non-superimposable mirror image, the two compounds can be easily differentiated.
In this structure, all the groups attached to the central carbon atom are the same. Therefore, it is a symmetric carbon which on rotation gives a superimposable mirror image.In a superimposable mirror image, the two compounds cannot be differentiated from each other.
Thus, the carbon atom marked with an asterisk sign shows that it is a quaternary alkane.
Note:
Quaternary carbon atoms are present in only those hydrocarbons which consist of at least five carbon atoms in the structure. Quaternary alkanes are only present in the branched form of alkane. The linear form of alkane does not show a quaternary structure. Quaternary alkanes are saturated compounds. They do not possess a double or triple bond.
