Question
Question: What is the mechanism of halogenations of alkanes?...
What is the mechanism of halogenations of alkanes?
Solution
Halogenation of alkanes means the substitution of a halogen atom(s) by the removal of one or more hydrogen atoms in the alkane. The mechanism of halogenations occurs in three steps: chain initiation, chain propagation, and chain termination.
Complete step by step answer:
When alkane is treated with a suitable halogen in the presence of ultraviolet light or by heating the reaction mixture to 520-670 K, haloalkane is produced.
For example, chlorination of methane. The reaction is given below:
methaneCH4+Cl2hvchloromethaneCH3Cl+HCl
chloromethaneCH3Cl+Cl2hvdichloromethaneCH2Cl2+HCl
dichloromethaneCH2Cl2+Cl2hvtrichloromethaneCHCl3+HCl
trichloromethaneCHCl3+Cl2hvtetrachloromethaneCCl4+HCl
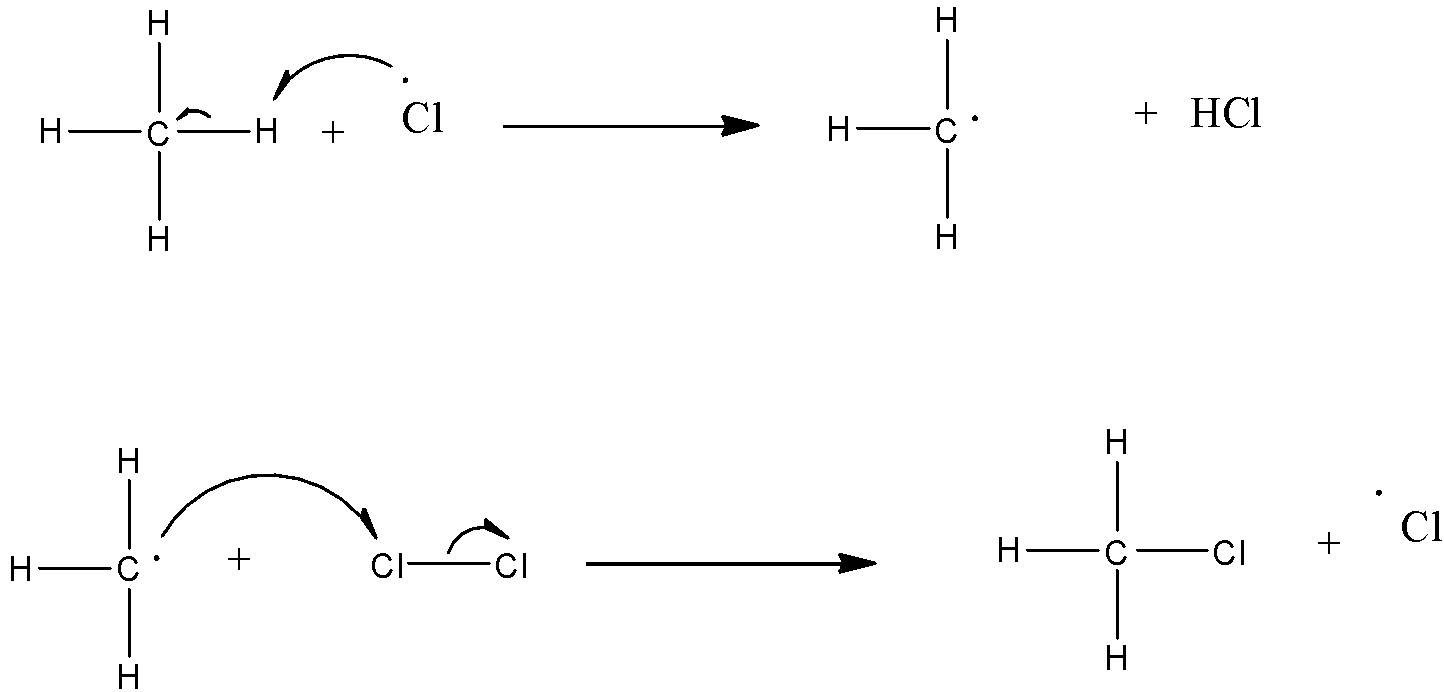
Mechanism of halogenations: The halogenations occur in three steps and it follows a free-radical mechanism.
(a)- Chain initiation: When a mixture of CH4and Cl2 is heated at 520-670 K in dark or is subjected to UV light at room temperature, Cl2 absorbs energy and undergoes homolytic fission which produces chlorine-free radicals.

(b)- Chain propagation: There are two steps in propagation. In the first reaction, the ∙Cl attacks the CH4 molecule and abstracts a hydrogen atom forming ∙CH3 and a molecule of HClas shown in reaction. In the second reaction, ∙CH3 thus produced reacts further with a molecule of Cl2 forming a molecule of methyl chloride and another ∙Cl. These reactions continue until the formation of CCl4.
CH3Cl+∙Cl→∙CH2Cl+HCl
∙CH2Cl+Cl2→CH2Cl2+∙Cl
CH2Cl2+∙Cl→∙CHCl2+HCl
∙CHCl2+Cl2→CHCl3+∙Cl
CHCl3+∙Cl→∙CCl3+HCl
∙CCl3+Cl2→CCl4+∙Cl
(c)- Chain termination: The chain reactions till now formed to have two types of free radicals combine to form molecules. The reaction is given below:
∙Cl+∙Cl→Cl−Cl
∙CH3+∙CH3→CH3−CH3
∙CH3+∙Cl→CH3−Cl
So, by following these steps the halogenations of an alkane are done.
Note: The order of reactivity of the halogens towards the halogenations reaction of alkanes as follows: F2 > Cl2 > Br2 > I2.The iodination reaction is reversible as follows:
CH4+I2⇌CH3−I+HI.
