Question
Question: What is the major function of ER? A. Fatty acid synthesis B. Steroid and cholesterol synthesis ...
What is the major function of ER?
A. Fatty acid synthesis
B. Steroid and cholesterol synthesis
C. Polypeptide formation
D. All of the above
Solution
The term ER represents endoplasmic reticulum. There are two types of endoplasmic reticulum in a cell. ER is only present in eukaryotic cells. ER is involved in the formation and synthesis of amino acids and lipids inside the cell.
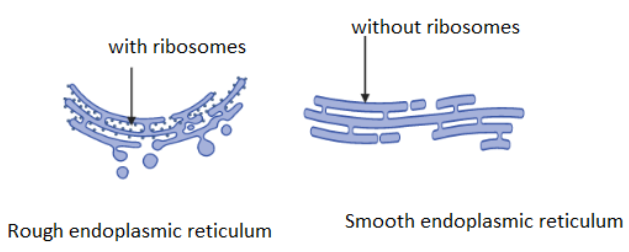
Complete answer: The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is a type of organelle found in the matrix of cell and is made up of two subunits – rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER), and smooth endoplasmic reticulum (SER). The endoplasmic reticulum attached with a ribosome is called a granular or rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER). It is abundant in cells and is engaged in active secretion and involves the formation of the polypeptide into the lumen of the endoplasmic reticulum. The absence of ribosomes on the surface of the endoplasmic reticulum is called a smooth endoplasmic reticulum or agranular endoplasmic reticulum (SER). There are different types of lipids secreted by the smooth endoplasmic reticulum. It also involves the synthesis of vitamins and carbohydrates and detoxification. The smooth endoplasmic reticulum is found in adipose tissue, muscle cells, glycogen metabolizing liver cells, and steroid hormones. Many general functions performed by the endoplasmic reticulum include the folding of protein molecules in sacks. These sacs are called cisternae.
So, option D: all of the above is the correct answer for the above-given question.
Note: Endoplasmic reticulum is absent in red blood cells (RBC), and spermatozoa. The unfolded protein response (UPR) is a type of cellular stress response that is related to the endoplasmic reticulum. The normal function of the cell is restored by UPR function which includes halting protein translation, degrading misfolded proteins, and activating the signaling pathways which lead to an increase in the production of molecular chaperones involved in protein folding.
