Question
Question: What is the kinetically controlled product in the following reaction? 
A.
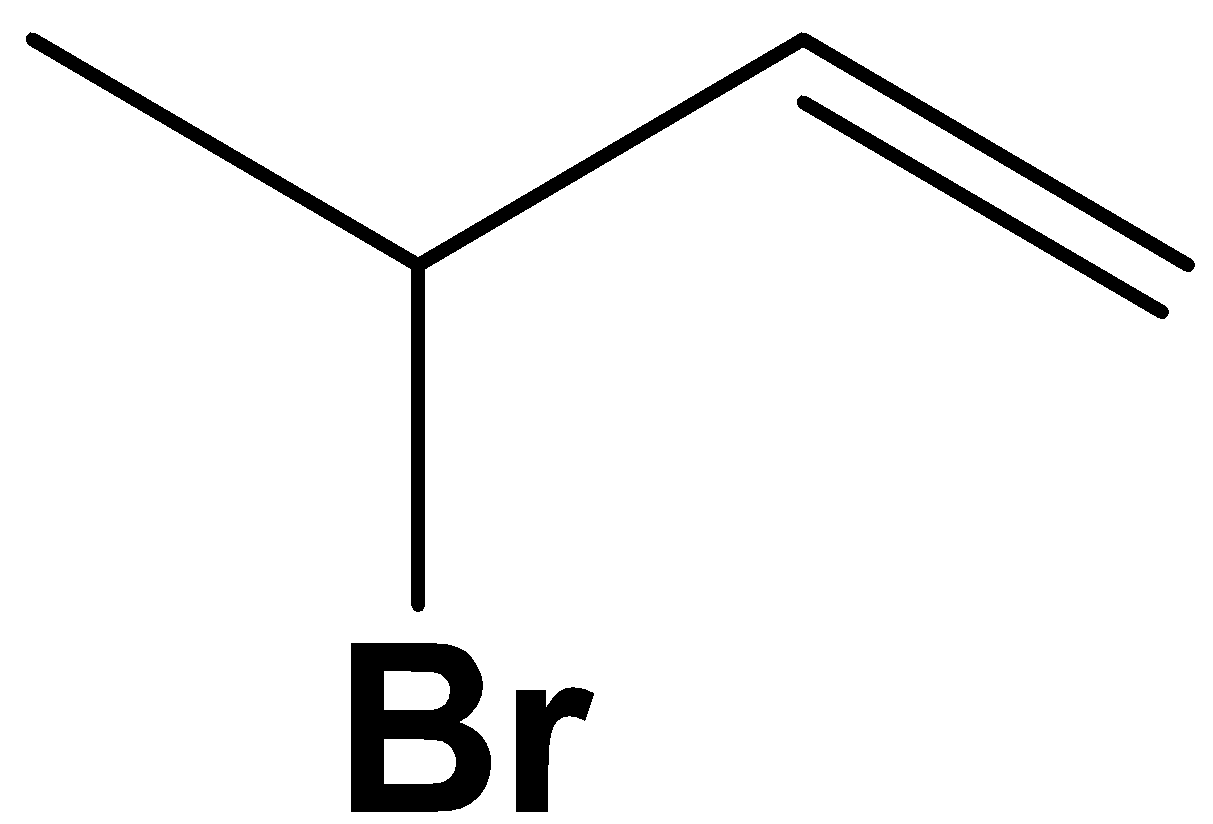
B.
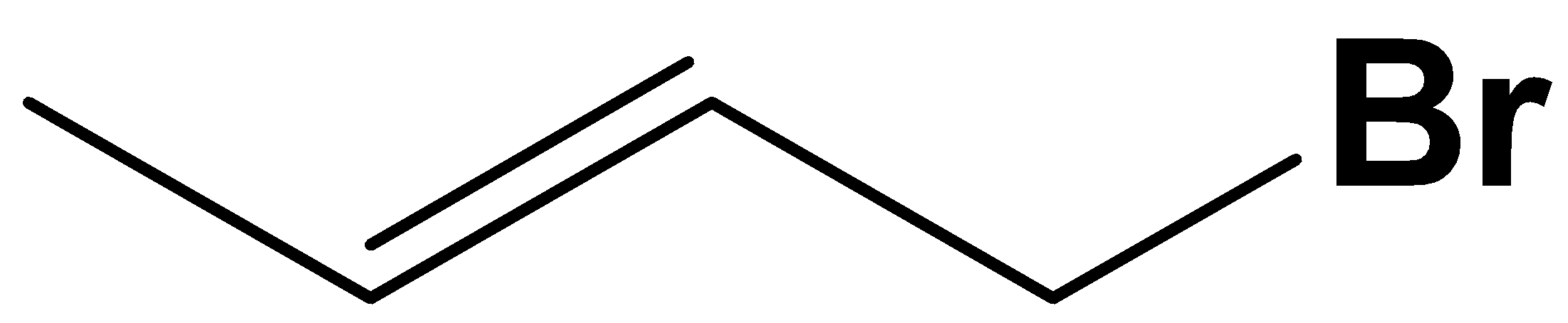
C.
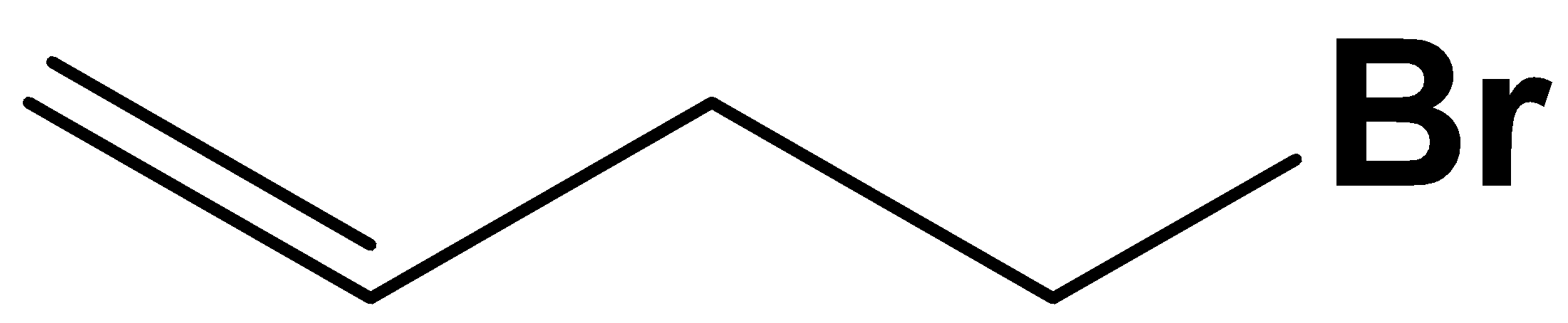
D.

Solution
The reaction of one equivalent of bromide with 1,3− butadiene provides a completely different} product under different reaction conditions and can be a classic example of the thought of thermodynamic versus kinetic control of a reaction. An electrophilic attack happens in the reaction. An electrophile is a chemical species that forms bonds with nucleophiles by accepting an electron pair. Since electrophiles accept electrons, they are Lewis acids.
Complete step by step answer:
Like non-conjugated dienes, conjugated dienes square measure subject to attack by electrophiles. Conjugated dienes expertise comparatively larger kinetic reactivity once reacted with electrophiles than non-conjugated dienes do. Upon electrophilic addition, the conjugated diene forms a mixture of 2 products—the kinetic product so the physical science product—whose quantitative relation is ready by the conditions of the reaction. A reaction yielding a lot of physical science products is purported to be beneath physical science management, and likewise, a reaction that yields a lot of kinetic products is beneath kinetic management.
Option A is that the kinetically controlled product inside the given reaction. 1,2− addition happens to relinquish kinetically controlled products.
Since addition happens across two consecutive carbons, we tend to often decision this “1,2 addition”
So the correct answer is choice A.
Note:
The reactivity of conjugated dienes (hydrocarbons that contain Two double bonds) varies depending on the locations of double bonds and temperature of the reaction. These reactions will manufacture each physical science and kinetic merchandise. Isolated double bonds give dienes with less stability thermodynamically than conjugated dienes. However, they are a lot reactive kinetically inside the presence of electrophiles and different reagents. This may be typically a result of Markovnikov addition to one of the double bonds. A carbocation is created once a bond is opened. This carbocation has two resonance structures and addition will occur at either of the positive carbons.
