Question
Question: What is the \( K \) in Hooke's law?...
What is the K in Hooke's law?
Solution
Hooke’s law states that the force needed to extend or compress a spring by some distance varies linearly to that distance. Hooke’s law is applicable within the valid elastic limit of the spring. It is functional within a very limited frame of reference as no material can be compressed or stretched beyond a certain minimum or maximum size.
Complete answer:
Suppose we take a simple helical spring whose one end is free.
We extend the free end by applying a force of magnitude F
Let x be the amount by which the free end is expanded from it’s relaxed position.
Now as Hooke’s law states that the force needed to extend or compress a spring by some distance varies linearly to that distance.
F α x
⇒F=−Kx
Where F is the restoring force or the spring force
K is the proportionality constant also known as spring constant
The value of K depends not only on the kind of elastic material under consideration but also on its dimensions and shape.
The negative sign in Hooke’s law implies that the spring force acts in the opposite direction of the applied force.
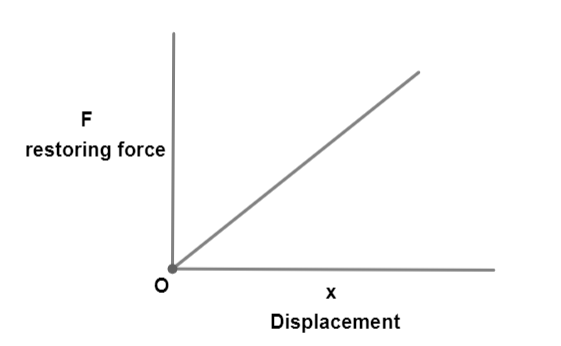
We can calculate the spring constant by plotting the graph between the restoring force F and the displacement of spring x
The graph will be a straight line and the slope of the graph gives the spring constant K
Note:
Hooke’s law ceases to apply past the elastic limit of a material and is accurate only for solid bodies if the forces and deformations are small. The law isn’t a universal principle and only applies to the materials as long as they aren’t stretched way past their capacity.
