Question
Question: What is the instantaneous rate of reaction? And how can we determine it?...
What is the instantaneous rate of reaction? And how can we determine it?
Solution
The term instantaneous rate means the reaction rate at a particular time of very short interval. We determine it with the help of plotting the reaction rate vs. time.
Complete step by step answer:
The instantaneous rate of reaction is the rate at some instant at a particular time. Specifically it is defined as the change in concentration of the components of a reaction at an infinitely small time interval. The average of the instantaneous reaction rate over a period of time gives the average rate during the reaction.
For determining the instantaneous rate at a definite time t we need to plot the change in rate of the rate of reaction along the x axis and the time interval along the y axis. Using the plot we calculate the negative of the slope of the curve of the change in concentration of a reactant with respect to the time at time t. It is done by measuring the slope of the tangent to the graph of concentration vs. time.
Let us consider a reaction in which a reactant R is converting into a product P. The reaction is
R→P
If we plot the change in the concentration of the formation of Pwith time t, we obtain a curved line instead of a straight line. The plot is as follows:
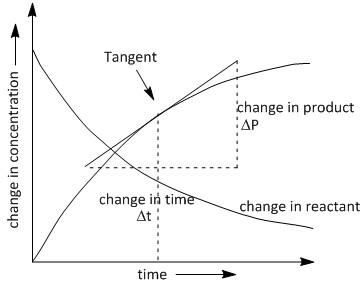
In the above graph we need to draw the best tangent at the time twhere we require the rate of reaction. By extending the endpoints of the tangent along the x and y axis we obtain a triangle where it is convenient to calculate the value of change in concentration of product P with time i.e. ΔtΔP .
The instantaneous rate of reaction is determined using the slope of the line or the tangent to the curve at any time (t).
Note:
The rate of concentration of products increases with time according to the plot seen above and the rate of concentration of reactants decreases with time. Thus a negative slope is obtained in plotting the change in concentration of reactant with time.
